- Different parts of the body perform specific functions. If any of these functions are disrupted, it indicates that something is not functioning properly within the body or there has been a change. This is often a symptom of a disease.
- Symptoms just indicate that there is a disease. They do not indicate the exact type of disease.
- Doctors often look for signs of a disease to determine the exact problem. These signs, unlike symptoms, are more definite indications of a disease. Sometimes, laboratory tests are also performed to diagnose a disease.
Topics
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Structure and Events
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Stamen (Male Reproductive Unit)
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Microsporangium
- Structure of Microspore Or Pollen Grain
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Pistil (Female Reproductive Unit)
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Megasporangium
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Formation of Embryo Sac
- Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Outbreeding Devices
- Pollen Pistil Interaction
- Fertilization Process
- Post Fertilisation in Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Endosperm
- Post Fertilization in Plant: Development of Embryo (Embryogeny)
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Apomixis
- Parthenocarpy
- Polyembryony
- Kinds of Pollination
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Animal
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Implantation in Human
- Pregnancy in Humans
- Placenta (Growth) in Human
- Parturition (Birth) in Human
- Lactation in Human
- Reproductive Health
- Population Stabilisation and Birth Control
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Infertility
- Gastrulation in humans
Inheritance and Variation
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Genes and Genetic
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Back Cross and Test Cross
- Deviations from Mendel’s Findings
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Linkage and Crossing Over
- Autosomal Inheritance
- Sex Linked Inheritance
- Sex Determination
- Genetic Disorders
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- The Genetic Material is a DNA
- Packaging of DNA Helix
- DNA Replication
- Protein Synthesis
- Regulation of Gene Expression
- Operon Concept
- Genomics
- Human Genome Project
- DNA Fingerprinting Technique
- Genetic Code
Origin and Evolution of Life
- Origin and Evolution of Universe and Earth
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Chemical Evolution of Life (Self-assembly Theory of the Origin of Life)
- Darwinism
- Mutation Theory
- Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
- Organic Evolution
- Hardy Weinberg’s Principle
- Adaptive Radiation
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Speciation
- Geological Time Scale
- Human Evolution
- Theories of Biological Evolution
Plant Water Relation
- Plant Water Relation
- Properties of Water
- Water absorbing organ
- Water Available to Roots for Absorption
- Means of Transport in Plants
- Concept of Imbibition
- Simple Diffusion
- Concept of Osmosis
- Osmotic Pressure
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis)
- Active Transport
- Passive Transport
- Water Potential (ψ)
- Path of Water Across the Root
- Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap)
- Transport of Mineral Ions
- Transport of Food
- Transpiration
- Types of Transpiration
- Structure of Stomatal Apparatus
- Significance of Transpiration
Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition
- Plant Growth
- Phases of Plant Growth
- Conditions Necessary for Plant Growth
- Plant Growth Rate
- Plant Growth Curve
- Differentiation, De-differentiation, Re- Differentiation
- Plant Development
- Plant Plasticity
- Plant Hormones
- Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Photoperiodism
- Vernalization (Yarovization)
- Plant Mineral Nutrition
- Nitrogen Cycle
Respiration and Circulation
- Respiration
- Organs of Respiratory Exchange
- Human Respiratory System
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Regulation of Breathing / Respiration
- Modified Respiratory Movements
- Disorders of Respiratory System
- Transportation in Living Organisms
- Circulation in Animals
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Human Heart
- Working mechanism of human heart
- Blood Vessels
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- Mechanism of respiration - Internal respiration
- Mechanism of respiration - External respiration
- Mechanism of respiration - Cellular respiration
Control and Co-ordination
- Control and Co-ordination
- Nervous System in Hydra
- Nervous System in Planaria (Flatworm)
- Neural Tissue
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Neuroglial Cells (Or Glial Cells)
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- The Spinal Cord
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Sensory Receptors
- Human Eye
- Human Ear
- Disorders of Nervous System
- Chemical Coordination
- Human Endocrine System
- The Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- The Pineal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Thymus Gland
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Reproductive Glands (Gonads)
- Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres
- Synapse - Types of synapse
- Transmission of nerve impulse
- Generation of nerve impulse
- Reflex Action
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Diffuse Endocrine Glands
Human Health and Diseases
- Defence System in Our Body: Immune System
- Immunity
- Types of Immunity
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Structure of Antibody
- Disease
- Protozoan Diseases
- Helminthic Diseases
- Bacterial Diseases
- Viral Diseases
- Fungal Diseases
- Vector Borne Diseases
- Cancer
- Adolescence
- Addiction
- Drug Abuse
Enhancement of Food Production
- Improvement in Food Production
- Plant Breeding
- Tissue Culture
- Single Cell Protein (SCP)
- Biofortification
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Animal Breeding
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Apiculture (Bee Farming)
- Pisciculture (Fish Farming)
- Sericulture
- Lac Culture
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Energy Generation
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Biofertilizers
Biotechnology
- Biotechnology
- Process and Principles of Biotechnology
- Methodology for rDNA Technology
- Commercial Applications of Biotechnology
- Bioethics
- Effects of Biotechnology on the Environment
- Biopatent and Biopiracy
- Transgenic Plants
- Transgenic animals
- Effects of Biotechnology on Human Health
- Tools and techniques for gene cloning/ rDNA technology
Organisms and Populations
- Organisms and the Environment Around
- Habitat
- Niche
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Population
- Population Interactions
- Organisms and Populations
Ecosystems and Energy Flow
- Ecosystem
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Classification of Animal
- Trophic Level
- Food Chain
- Food Web
- Ecological Pyramids
- Nutrient Cycles
- Ecological Succession
- Ecosystem Services
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Phosphorus Cycle
- Carbon Cycle
Biodiversity, Conservation and Environmental Issues
- Biodiversity
- Levels of Biodiversity
- Patterns of Biodiversity
- Biodiversity Current Scenario
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Conservation of Wildlife
- Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- Environmental Issues
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Noise Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Green House Effect
- Preventive Measures of Green House Effect
- Global Warming
- Preventive Measures of Global Warming
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Mission Harit Maharashtra
- Conservation of Biodiversity
Excretion and Osmoregulation
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Human Excretory System
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Regulation of Kidney Function
- Common Disorders of the Urinary System
Human Reproduction
- Introduction
- Identification of disease
Introduction:
The word is actually self-explanatory; we can think of it as ‘disease' or 'disturbed ease.' Disease, in other words, literally means being uncomfortable.
A disease is an abnormal condition that harms the structure and function of organs, tissues, or parts of a living organism. It’s important to note that a disease is not caused by a sudden external injury. Instead, it is a medical condition with specific signs and symptoms.
- Every disease has an origin. But there are certain diseases that are difficult to diagnose because of the confusing symptoms.
- The diseases may be autoimmune, bacterial, cancerous, digestive, sexually transmitted, etc. They can be cured by a number of strategies, such as antibiotics, other medications and surgeries.
- Antibiotics are the drugs that block the biochemical pathways of bacteria that cause diseases.
- These do not work against viral infections because the viruses depend upon the biochemical mechanisms of the host.
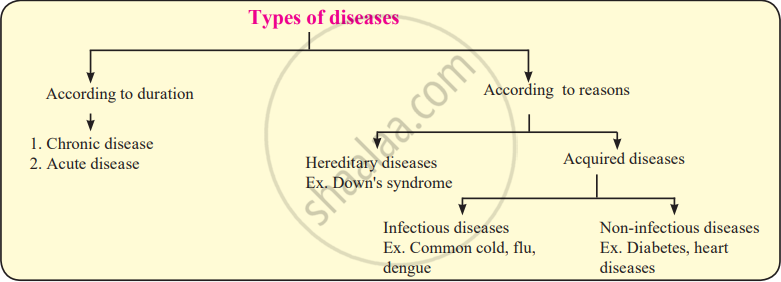
Identification of Disease:
A disease is associated with symptoms. In other words, our body shows certain indications with which we can assume that we may be suffering from a disease.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [103]
Match the following
| Rabies | Salmonella |
| Cholera | Yellow Urine |
| Tuberculosis | Cramps in legs |
| Hepatitis | Hydrophobia |
| Typhoid | Mycobacterium |
