Topics
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Structure and Events
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Stamen (Male Reproductive Unit)
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Microsporangium
- Structure of Microspore Or Pollen Grain
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Pistil (Female Reproductive Unit)
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Megasporangium
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Formation of Embryo Sac
- Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Outbreeding Devices
- Pollen Pistil Interaction
- Fertilization Process
- Post Fertilisation in Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Endosperm
- Post Fertilization in Plant: Development of Embryo (Embryogeny)
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Apomixis
- Parthenocarpy
- Polyembryony
- Kinds of Pollination
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Animal
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Implantation in Human
- Pregnancy in Humans
- Placenta (Growth) in Human
- Parturition (Birth) in Human
- Lactation in Human
- Reproductive Health
- Population Stabilisation and Birth Control
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Infertility
- Gastrulation in humans
Inheritance and Variation
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Genes and Genetic
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Back Cross and Test Cross
- Deviations from Mendel’s Findings
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Linkage and Crossing Over
- Autosomal Inheritance
- Sex Linked Inheritance
- Sex Determination
- Genetic Disorders
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- The Genetic Material is a DNA
- Packaging of DNA Helix
- DNA Replication
- Protein Synthesis
- Regulation of Gene Expression
- Operon Concept
- Genomics
- Human Genome Project
- DNA Fingerprinting Technique
- Genetic Code
Origin and Evolution of Life
- Origin and Evolution of Universe and Earth
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Chemical Evolution of Life (Self-assembly Theory of the Origin of Life)
- Darwinism
- Mutation Theory
- Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
- Organic Evolution
- Hardy Weinberg’s Principle
- Adaptive Radiation
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Speciation
- Geological Time Scale
- Human Evolution
- Theories of Biological Evolution
Plant Water Relation
- Plant Water Relation
- Properties of Water
- Water absorbing organ
- Water Available to Roots for Absorption
- Means of Transport in Plants
- Concept of Imbibition
- Simple Diffusion
- Concept of Osmosis
- Osmotic Pressure
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis)
- Active Transport
- Passive Transport
- Water Potential (ψ)
- Path of Water Across the Root
- Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap)
- Transport of Mineral Ions
- Transport of Food
- Transpiration
- Types of Transpiration
- Structure of Stomatal Apparatus
- Significance of Transpiration
Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition
- Plant Growth
- Phases of Plant Growth
- Conditions Necessary for Plant Growth
- Plant Growth Rate
- Plant Growth Curve
- Differentiation, De-differentiation, Re- Differentiation
- Plant Development
- Plant Plasticity
- Plant Hormones
- Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Photoperiodism
- Vernalization (Yarovization)
- Plant Mineral Nutrition
- Nitrogen Cycle
Respiration and Circulation
- Respiration
- Organs of Respiratory Exchange
- Human Respiratory System
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Regulation of Breathing / Respiration
- Modified Respiratory Movements
- Disorders of Respiratory System
- Transportation in Living Organisms
- Circulation in Animals
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Human Heart
- Working mechanism of human heart
- Blood Vessels
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- Mechanism of respiration - Internal respiration
- Mechanism of respiration - External respiration
- Mechanism of respiration - Cellular respiration
Control and Co-ordination
- Control and Co-ordination
- Nervous System in Hydra
- Nervous System in Planaria (Flatworm)
- Neural Tissue
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Neuroglial Cells (Or Glial Cells)
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- The Spinal Cord
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Sensory Receptors
- Human Eye
- Human Ear
- Disorders of Nervous System
- Chemical Coordination
- Human Endocrine System
- The Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- The Pineal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Thymus Gland
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Reproductive Glands (Gonads)
- Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres
- Synapse - Types of synapse
- Transmission of nerve impulse
- Generation of nerve impulse
- Reflex Action
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Diffuse Endocrine Glands
Human Health and Diseases
- Defence System in Our Body: Immune System
- Immunity
- Types of Immunity
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Structure of Antibody
- Disease
- Protozoan Diseases
- Helminthic Diseases
- Bacterial Diseases
- Viral Diseases
- Fungal Diseases
- Vector Borne Diseases
- Cancer
- Adolescence
- Addiction
- Drug Abuse
Enhancement of Food Production
- Improvement in Food Production
- Plant Breeding
- Tissue Culture
- Single Cell Protein (SCP)
- Biofortification
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Animal Breeding
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Apiculture (Bee Farming)
- Pisciculture (Fish Farming)
- Sericulture
- Lac Culture
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Energy Generation
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Biofertilizers
Biotechnology
- Biotechnology
- Process and Principles of Biotechnology
- Methodology for rDNA Technology
- Commercial Applications of Biotechnology
- Bioethics
- Effects of Biotechnology on the Environment
- Biopatent and Biopiracy
- Transgenic Plants
- Transgenic animals
- Effects of Biotechnology on Human Health
- Tools and techniques for gene cloning/ rDNA technology
Organisms and Populations
- Organisms and the Environment Around
- Habitat
- Niche
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Population
- Population Interactions
- Organisms and Populations
Ecosystems and Energy Flow
- Ecosystem
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Classification of Animal
- Trophic Level
- Food Chain
- Food Web
- Ecological Pyramids
- Nutrient Cycles
- Ecological Succession
- Ecosystem Services
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Phosphorus Cycle
- Carbon Cycle
Biodiversity, Conservation and Environmental Issues
- Biodiversity
- Levels of Biodiversity
- Patterns of Biodiversity
- Biodiversity Current Scenario
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Conservation of Wildlife
- Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- Environmental Issues
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Noise Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Green House Effect
- Preventive Measures of Green House Effect
- Global Warming
- Preventive Measures of Global Warming
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Mission Harit Maharashtra
- Conservation of Biodiversity
Excretion and Osmoregulation
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Human Excretory System
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Regulation of Kidney Function
- Common Disorders of the Urinary System
Human Reproduction
- Apiculture
- Types of Honey Bee
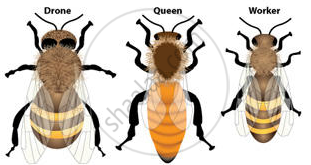
- Polymorphism in honey bee
- Artificial bee hive
Notes
Bee-keeping (Apiculture):
- Bee-keeping or apiculture is the maintenance of hives of honeybees for the production of honey.
- Bee-keeping is an age-old cottage industry.
- Although bees are active all year, they become lethargic in the winter and incredibly active in the spring.
- Honeybees are sociable insects with polymorphism and effective work division.
- A typical bee hive has a diameter of 30-90 cm. The number of bees in it is estimated to be in the 50-60 thousand range.
- Hive of Bees: One of the few tamed insects is the honey bee. Bee colonies are being raised in artificial wooden cages to maximise honey and wax output. The hive is an artificial box where the bee colony is kept and regulated.

- The apiary is the location where hives are kept and handled.
- The hives should be placed in an area with a lot of flowering plants.
- The environment should be tidy and free of offensive odours. Because each bee colony requires two glasses of water each day to survive, there should be clean drinking water nearby.
- Pollinators for sunflower, Brassica, apple, and pear include bees.
- A highly organised division of labour is found in the colony of the honey bee.
- Each colony has 40,000 to 50,000 individuals consisting of 3 casts - queens, drones and workers.
Important varieties of Honeybees:
- Apis dorsata, popularly known as the sarang bee, is a type of rock bee. It has the greatest size and generates the most honey. It is, however, a highly aggressive and migratory species that is not ideal for human keeping.
- Apis indica (Indian Mona-bee): This species is smaller than the sarang-bee and can be found throughout India. It has a gentle temperament, making it easy to control during rearing. Mona-bee hives produce approximately 3-4 kg of honey each hive.
- Apis florea (Bhringa-bee): This bee is the tiniest and most cautious of the species. Each hive barely produces roughly 250 grammes of honey. As a result, it is unsuitable for commercial use.
- Apis mellifera (European bee): Apis mellifera is a kind bee. It produces 9-10 times the amount of honey as the mona-bee. For commercial purposes, it is the most useful bee. By far the most important variant of this species is the Italian one.
Social Organization of Bees species:
- Queen bees: The queen bees are fertile females which lay thousands of eggs. Queen secretes Anti queen substance/Pheromones.
- Drones' bees: The drone bees are fertile males and their job is only to help in fertilizing the eggs laid by the queen.
- Worker's bees: Worker bees are sterile females who do the actual work of collecting nectar.
Useful products of Honey Bees:
-
Honey: Honey is a complex substance made when bees ingest nectar, process it, and store it into honeycombs. Honey is a food of high nutritive & indigenous medicinal value.

-
Beeswax (real product): Secretary product from a series of abdominal wax glands/hypodermal glands. Beeswax is used for the production of cosmetics and polishes.

-
Propolis: It is resinous mixture collected by bees from tree buds, flow saps etc. used as a sealant for unwanted open spaces of hives.

If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
