Topics
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Structure and Events
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Stamen (Male Reproductive Unit)
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Microsporangium
- Structure of Microspore Or Pollen Grain
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Pistil (Female Reproductive Unit)
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Megasporangium
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Formation of Embryo Sac
- Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Outbreeding Devices
- Pollen Pistil Interaction
- Fertilization Process
- Post Fertilisation in Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Endosperm
- Post Fertilization in Plant: Development of Embryo (Embryogeny)
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Apomixis
- Parthenocarpy
- Polyembryony
- Kinds of Pollination
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Animal
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Implantation in Human
- Pregnancy in Humans
- Placenta (Growth) in Human
- Parturition (Birth) in Human
- Lactation in Human
- Reproductive Health
- Population Stabilisation and Birth Control
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Infertility
- Gastrulation in humans
Inheritance and Variation
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Genes and Genetic
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Back Cross and Test Cross
- Deviations from Mendel’s Findings
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Linkage and Crossing Over
- Autosomal Inheritance
- Sex Linked Inheritance
- Sex Determination
- Genetic Disorders
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- The Genetic Material is a DNA
- Packaging of DNA Helix
- DNA Replication
- Protein Synthesis
- Regulation of Gene Expression
- Operon Concept
- Genomics
- Human Genome Project
- DNA Fingerprinting Technique
- Genetic Code
Origin and Evolution of Life
- Origin and Evolution of Universe and Earth
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Chemical Evolution of Life (Self-assembly Theory of the Origin of Life)
- Darwinism
- Mutation Theory
- Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
- Organic Evolution
- Hardy Weinberg’s Principle
- Adaptive Radiation
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Speciation
- Geological Time Scale
- Human Evolution
- Theories of Biological Evolution
Plant Water Relation
- Plant Water Relation
- Properties of Water
- Water absorbing organ
- Water Available to Roots for Absorption
- Means of Transport in Plants
- Concept of Imbibition
- Simple Diffusion
- Concept of Osmosis
- Osmotic Pressure
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis)
- Active Transport
- Passive Transport
- Water Potential (ψ)
- Path of Water Across the Root
- Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap)
- Transport of Mineral Ions
- Transport of Food
- Transpiration
- Types of Transpiration
- Structure of Stomatal Apparatus
- Significance of Transpiration
Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition
- Plant Growth
- Phases of Plant Growth
- Conditions Necessary for Plant Growth
- Plant Growth Rate
- Plant Growth Curve
- Differentiation, De-differentiation, Re- Differentiation
- Plant Development
- Plant Plasticity
- Plant Hormones
- Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Photoperiodism
- Vernalization (Yarovization)
- Plant Mineral Nutrition
- Nitrogen Cycle
Respiration and Circulation
- Respiration
- Organs of Respiratory Exchange
- Human Respiratory System
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Regulation of Breathing / Respiration
- Modified Respiratory Movements
- Disorders of Respiratory System
- Transportation in Living Organisms
- Circulation in Animals
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Human Heart
- Working mechanism of human heart
- Blood Vessels
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- Mechanism of respiration - Internal respiration
- Mechanism of respiration - External respiration
- Mechanism of respiration - Cellular respiration
Control and Co-ordination
- Control and Co-ordination
- Nervous System in Hydra
- Nervous System in Planaria (Flatworm)
- Neural Tissue
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Neuroglial Cells (Or Glial Cells)
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- The Spinal Cord
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Sensory Receptors
- Human Eye
- Human Ear
- Disorders of Nervous System
- Chemical Coordination
- Human Endocrine System
- The Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- The Pineal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Thymus Gland
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Reproductive Glands (Gonads)
- Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres
- Synapse - Types of synapse
- Transmission of nerve impulse
- Generation of nerve impulse
- Reflex Action
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Diffuse Endocrine Glands
Human Health and Diseases
- Defence System in Our Body: Immune System
- Immunity
- Types of Immunity
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Structure of Antibody
- Disease
- Protozoan Diseases
- Helminthic Diseases
- Bacterial Diseases
- Viral Diseases
- Fungal Diseases
- Vector Borne Diseases
- Cancer
- Adolescence
- Addiction
- Drug Abuse
Enhancement of Food Production
- Improvement in Food Production
- Plant Breeding
- Tissue Culture
- Single Cell Protein (SCP)
- Biofortification
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Animal Breeding
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Apiculture (Bee Farming)
- Pisciculture (Fish Farming)
- Sericulture
- Lac Culture
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Energy Generation
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Biofertilizers
Biotechnology
- Biotechnology
- Process and Principles of Biotechnology
- Methodology for rDNA Technology
- Commercial Applications of Biotechnology
- Bioethics
- Effects of Biotechnology on the Environment
- Biopatent and Biopiracy
- Transgenic Plants
- Transgenic animals
- Effects of Biotechnology on Human Health
- Tools and techniques for gene cloning/ rDNA technology
Organisms and Populations
- Organisms and the Environment Around
- Habitat
- Niche
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Population
- Population Interactions
- Organisms and Populations
Ecosystems and Energy Flow
- Ecosystem
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Classification of Animal
- Trophic Level
- Food Chain
- Food Web
- Ecological Pyramids
- Nutrient Cycles
- Ecological Succession
- Ecosystem Services
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Phosphorus Cycle
- Carbon Cycle
Biodiversity, Conservation and Environmental Issues
- Biodiversity
- Levels of Biodiversity
- Patterns of Biodiversity
- Biodiversity Current Scenario
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Conservation of Wildlife
- Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- Environmental Issues
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Noise Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Green House Effect
- Preventive Measures of Green House Effect
- Global Warming
- Preventive Measures of Global Warming
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Mission Harit Maharashtra
- Conservation of Biodiversity
Excretion and Osmoregulation
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Human Excretory System
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Regulation of Kidney Function
- Common Disorders of the Urinary System
Human Reproduction
- Introduction
- Some Sexually Transmitted Diseases
- Other diseases of the Reproductive Tract
Introduction:
STDs or Venereal Diseases (VDs) are reproductive tract infections (RTI) that are transmitted from one human being to another through sexual intimacy. Of these, HIV/AIDS and Hepatitis B are also transmitted through sharing surgical instruments, injection needles, transfusion of blood, and congenitally transferred from mother to foetus via placenta or milk.
Except for AIDS, Hepatitis B, and Genital Herpes, all other STDs are completely curable if detected and treated early. In women, they are often asymptomatic and remain undetected for long. Delay in reporting can lead to Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases (PID), and abortion. Still birth, ectopic pregnancy, infertility, and even cancer of the reproductive tract. Incidence of STDs is especially high in the age group of 15-24 years.
Some Sexually Transmitted Diseases:
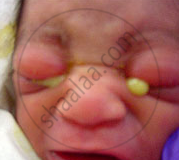
1) Gonorrhoea: Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is spread through sexual contact and use of common toilets and undergarments. Incubation period 2-5 days Passes through genital tubes, forms pus-containing discharges, pain over genitalia, and burning during urination. It may also lead to arthritis and eye infection in children of affected mothers. Detection: Gram staining of discharge and culture.
|
Gonorrhea signs and symptoms |
Gonorrhea infected children |
2) Genital Herpes:
It is caused by the Type-II Herpes simplex virus. The disease is primarily transmitted sexually through genital secretions but also on contact with viroids and genitalia. There are vesiculopustular lesions followed by clusters of painful erythematous ulcers over external genitalia and perianal regions. Symptoms are more severe in females. Infection of neonates can occur in the case of infected females. There is fever, headache pain, itching, and vaginal and urethral discharge with tender inguinal lymphadenopathy (swelling of lymph nodes). Urethral and cervix infections also occur. Detection is carried out by clinical symptoms, antigen detection, PCR, and nucleic acid hybridization.
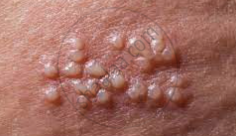
Genital Herpes
3) Syphilis: It is a highly infectious venereal bacterial disease caused by a spirochaete (Treponema pallidum) with an incubation period of 3-5 weeks. Transmission occurs through sexual contact and from mother to child. In the 1st stage, there is an indurated infectious and painless ulcer or chancre on the genitals and swelling of local lymph glands. In the 2nd stage, the chancre is healed and there are skin lesions, rashes, hair loss, swollen joints, and flu-like illness occasionally. In the tertiary stage, chronic ulcers appear on the palate, nose, and lower leg. These can be paralysis, brain damage, blindness, etc.
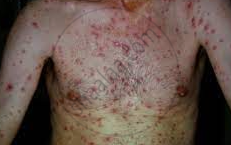
Syphilis
4) Hepatitis B: It is caused by the hepatitis B virus. Modes of transmission may be blood transfusion, sexual contact, saliva, tears, intravenous drug abuse, tattooing, ear, and nose piercing, and sharing of razors. It can produce cirrhosis and possibly cancer of the liver. Vaccines produced through recombinant DNA technology are available to prevent hepatitis B infection. E.g., Recombivax HB.
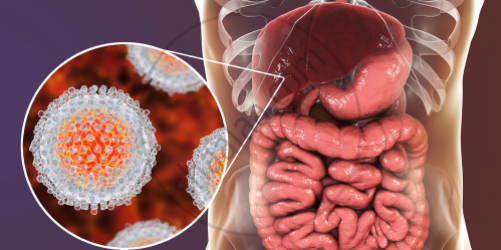
Hepatitis B
5) Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDs):
It is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). HIV is a retrovirus that attacks helper T cells, which stimulate antibody production of B cells. This results in the loss of natural defense against viral infection.
The diagnosis of AIDS cannot be confirmed without tests in medical laboratories. The ELISA test is used for its proper diagnosis. The symptoms of AIDS are person-specific.
HIV was first reported in an African species of monkey. According to the National AIDS Control Program and UNAIDS, 80 – 85% HIV infections in India occur through unsafe sexual contacts.
- AIDS does not occur due to touching and sharing food with an HIV-infected person or by nursing the HIV patient.
- Our behaviour with HIV-infected people must be normal.


Steps to prevent STDs:
- Avoid sex with unknown/multiple partners.
- Always use condoms during coitus.
- If in doubt, go to a qualified doctor for early detection and treatment for diseases.
Other diseases of the Reproductive Tract:
1) Testicular Cancer: Most common cancer in males of age 20-35 years. 95% of cases arise from spermatogenic cells within seminiferous tubules. An early sign is a mass in the testis, often associated with a sensation of testicular heaviness or a dull ache in the lower abdomen. The pain usually does not occur.
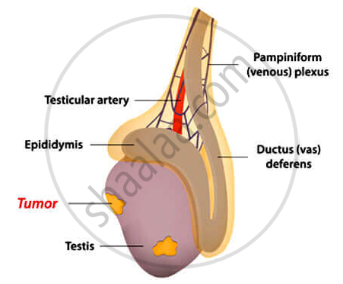
Testicular Cancer
2) Prostate Disorders: Any infection, enlargement, or tumour that obstructs the urine flow. Acute and chronic infections of the prostate are common in pot-pubescent males often in associated with inflammation of the urethra. It is one of the leading causes of death from cancer in men. A blood test can measure levels of Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA).
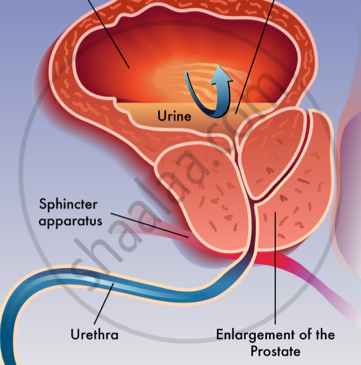
Enlarged prostate
3) Pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS): Appears in the post-ovulatory period and disappears as soon as menses begins. Signs are highly variable. They may include oedema, weight gain, breast swelling and tenderness, abdominal distensions, backache, joint pain, constipation, fatigue, lethargy, etc.
4) Breast cancer: Breast cancer is a disorder in which the cells of the breast proliferate uncontrollably. There are various types of breast cancer. The type of breast cancer is determined by which cells in the breast develop into cancer. A lump or thickening in the breast that feels distinct from the surrounding tissue. Breast size, shape, or appearance changes. Dimpling is a change in the skin above the breast. A recently flipped nipple. The pigmented region of skin surrounding the nipple (areola) or breast flesh peeling, scaling, crusting, or flaking. Redness or pitting of the skin around your breast, similar to orange skin. Drugs like Tamoxifen and Evista are used for prevention.
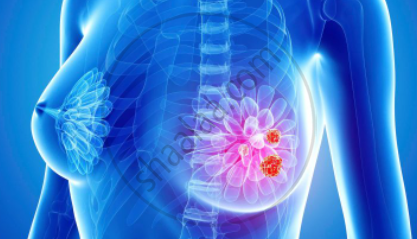
Breast cancer
5) Cervical Cancer: Cervical cancer is caused by the Human Papillomavirus, which is transmitted sexually (HPV). HPV can induce abnormal cervical cell proliferation, often known as cervical dysplasia. Pelvic pain increased vaginal discharge, and irregular vaginal bleeding is the most prevalent symptoms and indicators of cervical cancer.
- Having several sexual partners is a risk factor for cervical cancer.
- Prolonged use of birth control tablets and a Papanicolaou smear (PAP smear) paired with an HPV test can be used to diagnose cervical cancer.
- To assess the stage of cancer, X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans may be performed. Cervical cancer treatment options include radiation therapy, surgery, and chemotherapy.
- Precancerous alterations in the cervix can be detected using modern screening procedures. As a result, screening is suggested once a year for women over the age of 30.
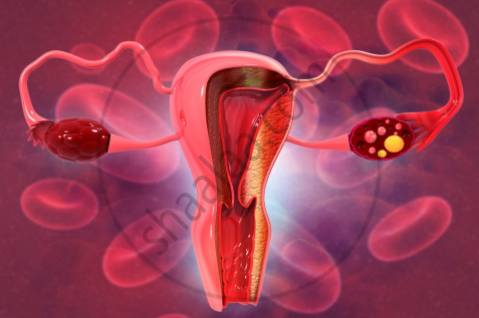
Cervical cancer