Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram, mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
Solution
(a)
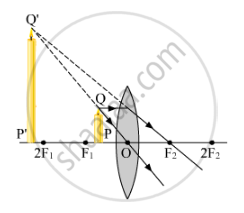
(b) The object distance (u) and the image distance (v) are indicated in the figure given below. Since both the image and the object lie in the direction opposite to the direction of the incoming ray, both of them will be negative. The relation between (u), (v) and (f) given by the lens formula is
`1/f=1/v-1/u`
As both (u) and (v) are negative, the above equation will be changed to
`1/f=1/((-v))-1/((-u))`
`1/f=-1/v+1/u`
`1/f=1/u-1/v`

(c) Given:
u = −20 cm
m = −1
Since magnification is given as
`m=v/u`
`rArrv=`
Focal length can be calculated as
`1/f=1/v=1/u=1/20-1/((-20))=1/10`
`rArrf=10`
Thus, the power of the convex lens is
`p=1/f(m)=100/10=10`
RELATED QUESTIONS
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations :
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –100 | +25 |
| 2 | –60 | +30 |
| 3 | –40 | +40 |
| 4 | –30 | +60 |
| 5 | –25 | +100 |
| 6 | –15 | +120 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c) Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No. 2. Also find the approximate value of magnification.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from air into an optically denser medium.
Three convex lenses are available having focal lengths of 4 cm, 40 cm and 4 m respectively. Which one would you choose as a magnifying glass and why?
A burning candle whose flame is 1.5 cm tall is placed at a certain distance in front of a convex lens. An image of candle flame is received on a white screen kept behind the lens. The image of flame also measures 1.5 cm. If f is the focal length of convex lens, the candle is placed:
(a) at f
(b) between f and 2f
(c) at 2f
(d) beyond 2f
A convex lens of focal length 6 cm is held 4 cm from a newspaper which has print 0.5 cm high. By calculation, determine the size and nature of the image produced.
What type of images can a convex lens make?
What kind of lens can form:
an inverted diminished image?
Which part causes the greatest convergence?
What kind of lens is used to correct
long-sightedness?
