Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram, mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
उत्तर
(a)
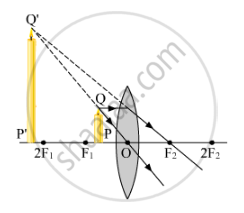
(b) The object distance (u) and the image distance (v) are indicated in the figure given below. Since both the image and the object lie in the direction opposite to the direction of the incoming ray, both of them will be negative. The relation between (u), (v) and (f) given by the lens formula is
`1/f=1/v-1/u`
As both (u) and (v) are negative, the above equation will be changed to
`1/f=1/((-v))-1/((-u))`
`1/f=-1/v+1/u`
`1/f=1/u-1/v`

(c) Given:
u = −20 cm
m = −1
Since magnification is given as
`m=v/u`
`rArrv=`
Focal length can be calculated as
`1/f=1/v=1/u=1/20-1/((-20))=1/10`
`rArrf=10`
Thus, the power of the convex lens is
`p=1/f(m)=100/10=10`
संबंधित प्रश्न
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

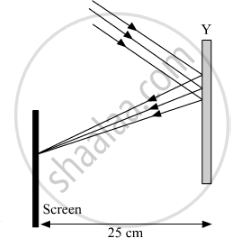
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
If an object is at a considerable distance (or infinity) in front of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
What kind of lens is used to correct
long-sightedness?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is of the same size as the object?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
Complete the following table:
| Type of lens | Position of object | Nature of image | Size of image |
| Convex | Between optical centre and focus | ||
| Convex | At focus | ||
| Concave | At infinity | ||
| Concave | At any distance |
How will you decide whether a given piece of glass is a concave lens, convex lens, or a plane glass plate?
Can a normal convex lens behave like a concave lens and vice-versa?
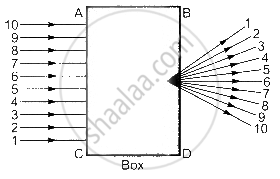
A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the holes on the other face of the box as show in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?