Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

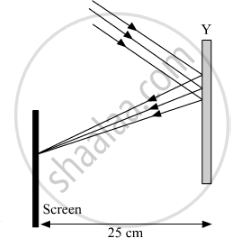
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
उत्तर
Device X is convex lens. This is because for a convex lens light rays which are parallel to each other but not to the principle axis meet on the focal plane. Also, the distance between the focal plane and the lens gives the focal length of the lens. Thus the focal length of the device X is 20 cm.
Device Y is concave mirror. This is because for a concave mirror light rays which are parallel to each other but not to the principle axis meet on the focal plane. Also, the distance between the focal plane and the lens gives the focal length of the mirror. Thus the focal length of the device Y is 25 cm.
Hence, the correct answer is Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
To find the image-distance for varying object-distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image of the screen.
(a) In which direction – towards or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image – does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a real magnified image by a convex lens. (In your sketch the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus of lens should be shown clearly).
A convex lens of focal length 8 cm forms a real image of the same size as the object. The distance between object and its image will be:
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 32 cm
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
A convex lens of focal length 6 cm is held 4 cm from a newspaper which has print 0.5 cm high. By calculation, determine the size and nature of the image produced.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
- In which type of microscope do you find the lens arrangement as shown in the following diagram?

- Write about the working and the use of this microscope.
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex lens.
