Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
विकल्प
At the principal focus of the lens
At twice the focal length
At infinity
Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus
उत्तर
At twice the focal length
Explanation:
The object is to be placed at twice the focal length of the lens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

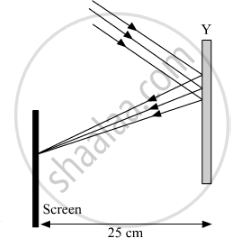
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
If an object is at a considerable distance (or infinity) in front of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
How could you find the focal length of a convex lens rapidly but approximately?
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
Three convex lenses are available having focal lengths of 4 cm, 40 cm and 4 m respectively. Which one would you choose as a magnifying glass and why?
An object is placed f and 2f of a convex lens. Which of the following statements correctly describes its image?
(a) real, larger than the object
(b) erect, smaller than the object
(c) inverted, same size as object
(d) virtual, larger than the object
An object 3 cm high is placed 24 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find by calculations, the position, height and nature of the image.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Figure below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and a prism respectively. In each diagram, label the incident, refracted emergent rays and the angle of deviation.

A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations:
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –60 | +12 |
| 2 | –30 | +15 |
| 3 | –20 | +20 |
| 4 | –15 | +30 |
| 5 | –12 | +60 |
| 6 | –9 | +90 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? State reason for your answer.
(b) For what object-distance (u) is the corresponding image-distance (v) not correct? How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(c) Choose an appropriate scale to draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
When you focus the image of a distant flag, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image as it appears on the screen is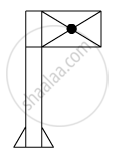
(A)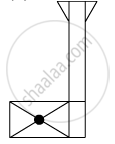
(B)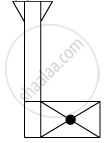
(C)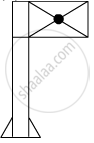
(D)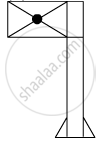
An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find (i) the position (ii) the magnification and (iii) the nature of the image formed.
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real image of the same size
How will you determine the focal length of a convex lens by the plane mirror method?
Define the terms principal foci and focal lengths as applied to a convex lens, and show them with the help of proper diagrams.

The above image shows a thin lens with a focal length of 5m.
- What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
- If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed.
- Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii).
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
