Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
विकल्प
Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature
At the centre of curvature
Beyond the centre of curvature
Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
उत्तर
Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Explanation:
For a virtual, erect and larger image, the object must lie between the pole of the mirror and its focus.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
Find the focal length of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Draw a ray diagram showing how a concave mirror can be used to produce a real, inverted and diminished image of an object.
The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
(a) between centre of curvature and focus
(b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
(c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(d) at a distance equal to focal length
One of the following does not apply to a concave mirror this is:
(a) focal length is negative
(b) image distance can be positive or negative
(c) image distance is always positive
(d) height of image can be positive or negative
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
If the object is moved further away from the mirror, what changes are there in the position and size of the image?
Between which two points of concave mirror should an object be placed to obtain a magnification of:
(a) −3
(b) +25
(c) −0.4
What type of image/images are formed by:
a convex mirror?
The mirror which can form a magnified image of an object is:
(a) convex mirror
(b) plane mirror
(c) concave mirror
(d) both convex and concave mirror
If the radius of curvature of a concave mirror is 20 cm, its focal length is:
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
A _____________ mirror is used by a dentist.
In which equipment/s do you find ___________________
Large ______ mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
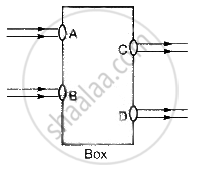
Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
The mirror having reflection surface curved outward ______.
A concave mirror produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed ______.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Head lamps of a car
