Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
उत्तर
Two light rays whose path of refection are priorly know are:
(i) The incident ray passes through the centre of curvature: In this case, light after reflecting from the concave mirror moves back in the same path. This happens because light is incident perpendicularly on the mirror surface.
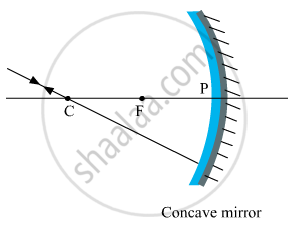
(ii) The ray incident obliquely to the principal axis: In this case, the incident ray will be reflected back by the reflecting surface of the concave mirror obliquely and making equal angles with the principal axis.

Let an object "a candle" is placed between the focus and pole of the concave mirror. Then using above two rays, image of the candle can be located as shown below:
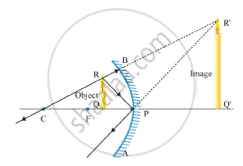
In this case, the image is formed behind the mirror. This image is virtual, erect and magnified.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which type of mirror is used by a dentist?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Parallel rays of light are reflected by a concave mirror to a point called the ..........
What is a spherical mirror? Distinguish between a concave mirror and a convex mirror.
The diagram shows a dish antenna which is used to receive television signals from a satellite. The antenna (signal detector) is fixed in front of the curved dish.
Figure
(a) What is the purpose of the dish?
(b) Should it be concave or convex?
(c) Where should the antenna be positioned to receive the strongest possible signals?
(d) Explain what change you would expect in the signals if a larger dish was used.
A student obtained a sharp inverted image of a distant tree on a screen placed in front of the concave mirror. He then removed the screen and tried to look into the mirror. He would now see
(A) a very blurred image on the wall opposite to the mirror
(B) an erect and magnified image of the tree in the mirror
(C) no image as the screen has been removed
(D) a highly diminished inverted image of the tree at the focus of the mirror.
A concave mirror of radius 30 cm is placed in water. It’s focal length in air and water differ by ______.
You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
You are provided with a convex mirror, a concave mirror, a convex lens and a concave lens. You can get an inverted image from
A student wants to obtain an erect image of an object using a concave mirror of 10 cm focal length. What will be the distance of the object from mirror?
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Shaving mirror
