Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A student obtained a sharp inverted image of a distant tree on a screen placed in front of the concave mirror. He then removed the screen and tried to look into the mirror. He would now see
(A) a very blurred image on the wall opposite to the mirror
(B) an erect and magnified image of the tree in the mirror
(C) no image as the screen has been removed
(D) a highly diminished inverted image of the tree at the focus of the mirror.
उत्तर
The student would observe a highly diminished inverted image of the tree at the focus of the mirror.
The Correct Answer is D
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
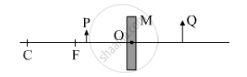
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
With the help of a ray diagram, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a virtual image by a converging mirror.
Mark clearly the pole, focus, centre of curvature and position of object in each case.
What kind of mirror can have a focal length of, −20 cm?
Write down a formula for the magnification produced by a concave mirror.
in terms of height of object and height of image
If an object of 10 cm height is placed at a distance of 36 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm, find the position, nature and height of the image.
An object is placed 15 cm from (a) a converging mirror, and (b) a diverging mirror, of radius of curvature 20 cm. Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
To construct ray diagram we use two light rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection. Use these rays to locate the image of an object placed between centre of curvature and focus of a concave mirror.
