Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
उत्तर
A convex mirror always produces an erect and diminished image of the object placed in front of it irrespective of the position of the object.
Consider a case in which an object is placed anywhere between pole (P) and infinity in front of a convex mirror. The ray diagram is as shown:-
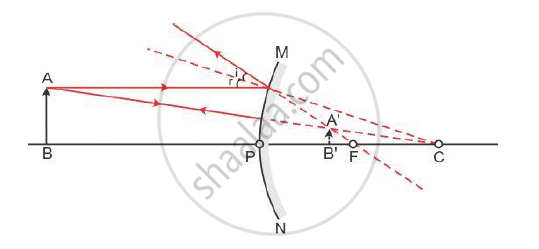
A virtual, erect and diminished image will be formed behind the mirror between the pole (P) and focus (F) of the mirror.
As a convex mirror gives a wide field of view, it is used as a rear view mirror in vehicles.
It enables the driver to view a much larger area of the traffic behind. It is also used as shop security mirrors.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Three students A, B and C focussed a distant building on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. To determine focal length of the concave mirror they measured the distances as given below:
Student A : From mirror to the screen
Student B : From building to the screen
Student C : From building to the mirror
Who measured the focal length correctly ;
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a mirror is formed on a screen placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from its pole. What is the nature of the mirror? Find its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm, find the height of its image. State whether the image formed is erect or inverted
A communications satellite in orbit sends a parallel beam of signals down to earth. If these signals obey the same laws of reflection as light and are to be focussed onto a small receiving aerial, what should be the best shape of the metal 'dish' used to collect them?
For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms a real image equal in size to the object?
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a convex mirror?
If a concave mirror has a focal length of 10 cm, find the two positions where an object can be placed to give, in each case, an image twice the height of the object.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between the focus and centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
The mirror having reflection surface curved outward ______.
A concave mirror of radius 30 cm is placed in water. It’s focal length in air and water differ by ______.
Identify the device used as a spherical mirror or lens in following case, when the image formed is virtual and erect in case.
Object is placed between device and its focus, image formed is enlarged and behind it.
