Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
उत्तर
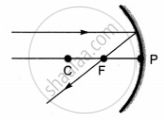
A convex mirror always produces an erect and diminished image of the object placed in front of it irrespective of the position of the object.
Consider a case in which an object is placed anywhere between pole (P) and infinity in front of a convex mirror. The ray diagram is as shown:-
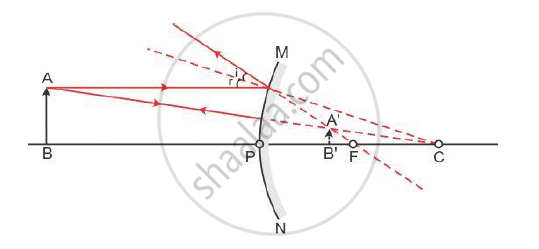
A virtual, erect and diminished image will be formed behind the mirror between the pole (P) and focus (F) of the mirror.
As a convex mirror gives a wide field of view, it is used as a rear view mirror in vehicles.
It enables the driver to view a much larger area of the traffic behind. It is also used as shop security mirrors.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 48 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the flame at a distance of 12 cm from its pole.
(a) Suggest the type of mirror he should use.
(b) Find the linear magnification of the image produced.
(c) How far is the image from its object?
(d) Draw ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed, so that a sharp focused image can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
The angle between an incident ray and the plane mirror is 30°. The total angle between the incident ray and reflected ray will be:
(a) 30°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 120°
The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
(a) between centre of curvature and focus
(b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
(c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(d) at a distance equal to focal length
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Calculate the image distance.
A large concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 1.5 m. A person stands 10 m in front of the mirror. Where is the person's image?
If a concave mirror has a focal length of 10 cm, find the two positions where an object can be placed to give, in each case, an image twice the height of the object.
Which of the following are concave mirrors and which convex mirrors?
Give any two applications of a concave and convex mirror.
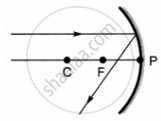
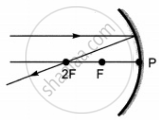
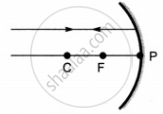
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?

 |
 |
 |
 |
| A | B | C | D |
