Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
उत्तर
The two rays chosen to construct a ray diagram are shown in the ray diagram given below

(i) Ray I: When the incident ray is parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray will pass through the focus of concave mirror or it appears to pass through the focus of convex mirror.
(ii) Ray II: When the incident ray passes through or appears to pass through the centre of curvature, the light, after reflection from the spherical mirror, reflects back along the same path.
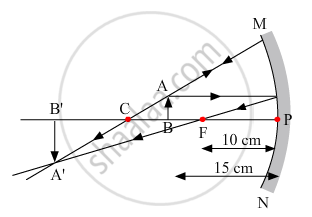
The image formed is real, inverted and magnified. It is formed beyond the centre of curvature.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Headlights of a car
Support your answer with reason.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
A concave mirror .......... rays of light whereas convex mirror ............ rays
ill in the following blank with suitable word:
For a convex mirror, parallel rays of light appear to diverge from a point called the ......... .
An object is 100 mm in front of a concave mirror which produces an upright (erect image). The radius of curvature of the mirror is ______.
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a concave mirror?
Between which two points of concave mirror should an object be placed to obtain a magnification of:
(a) −3
(b) +25
(c) −0.4
The mirror which can form a magnified image of an object is:
(a) convex mirror
(b) plane mirror
(c) concave mirror
(d) both convex and concave mirror
A concave mirror of radius 30 cm is placed in water. It’s focal length in air and water differ by ______.
Identify the device used as a spherical mirror or lens in following case, when the image formed is virtual and erect in case.
Object is placed between device and its focus, image formed is enlarged and behind it.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Head lamps of a car
