Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
Solution
Two light rays whose path of refection are priorly know are:
(i) The incident ray passes through the centre of curvature: In this case, light after reflecting from the concave mirror moves back in the same path. This happens because light is incident perpendicularly on the mirror surface.
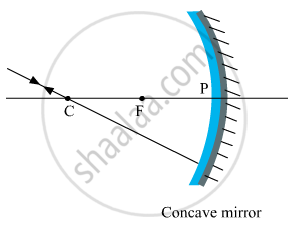
(ii) The ray incident obliquely to the principal axis: In this case, the incident ray will be reflected back by the reflecting surface of the concave mirror obliquely and making equal angles with the principal axis.

Let an object "a candle" is placed between the focus and pole of the concave mirror. Then using above two rays, image of the candle can be located as shown below:
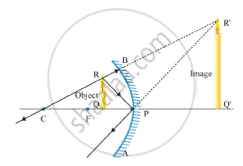
In this case, the image is formed behind the mirror. This image is virtual, erect and magnified.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Study the following diagram and select the correct statement about the device 'X' :

(A) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(B) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 6 cm
(C) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm
(D) Device 'X' is a convex of mirror of focal length 12 cm
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification −1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror:
(i) Write the type of mirror.
(ii) What is the nature of the image formed?
(iii) How far is the object located from the mirror?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image with the help of suitable rays:
What is the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an object? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror.
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
State two characteristics of the image formed.
A converging mirror forms a real image of height 4 cm of an object of height 1 cm placed 20 cm away from the mirror:
(i) Calculate the image distance.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror?
Name the mirror which can give:
an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light from a bulb falls on it?
(a) concave mirror as well as concave lens
(b) convex mirror as well as concave lens
(c) concave mirror as well as convex lens
(d) concave mirror as well as convex lens
Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
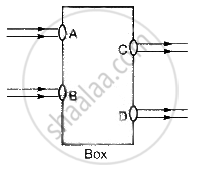
You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
