Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A converging mirror forms a real image of height 4 cm of an object of height 1 cm placed 20 cm away from the mirror:
- Calculate the image distance.
- What is the focal length of the mirror?
Solution
A concave mirror is a converging mirror.
Distance of the object from the mirror μ = −20 cm
Height of the object ho = 1 cm
Height of the image hi = v4 cm
We have to find the distance of the image v and the focal length of the mirror f.
Using the magnification formula, we get
`m = h_i/h_o = (-v)/u`
⇒ `(-4)/1 = (-v)/-20`
`v = 20 xx (-4)/1 = -80` cm
Thus, the distance of the image v is 80 cm.
Now, using the mirror formula, we get
`1/f = 1/v + 1/u`
`1/f = 1/-80 + 1/-20`
= `-1/80 -4/80`
= `-5/80`
`1/f = -1/16`
f = −16 cm
Thus, the focal length of the concave mirror is −16 cm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
A concave mirror .......... rays of light whereas convex mirror ............ rays
What kind of mirror can have a focal length of, −20 cm?
A bright object 50 mm high stands on the axis of a concave mirror of focal length 100 mm and at a distance of 300 mm from the concave mirror. How big will the image be?
Complete the following diagrams in figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2 if F is the focus and C is the centre of curvature.
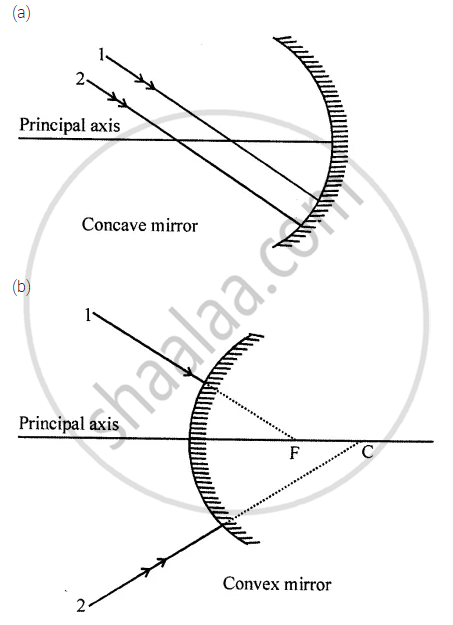
State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement.
When an object is at the centre of curvature of concave mirror the image formed will be virtual and erect.
You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
In the headlights of motor vehicles, ______ mirrors are used as reflectors.
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
