Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Solution
(a) In case (I), object is beyond C. For concave ‘mirrors, when the object is outside C, the image will be between C and F, and the image will be inverted and diminished (smaller than the object).
(b) In case (II), object is at C, so the image formed will be real and of same size.
(c) The dentist positions a small concave mirror so that the tooth is in focus. The dentist then examines a magnified image of the tooth in the concave mirror. Because the tooth seems considerably larger in the concave mirror, the dentist may easily check the tooth defect.
OR
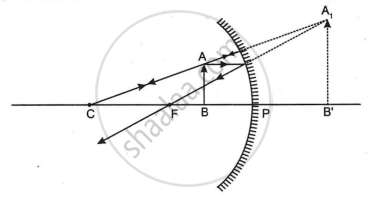
(c) We are aware that a virtual and expanded picture is created when an object is positioned between P and F of a concave mirror. As a result, we can properly shave using a concave mirror because the microscopic hairs are easily visible.
In scenario (III), the object is positioned between F and P, simulating the use of concave mirrors as shaving mirrors.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object of height 5 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. If the distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 20 cm, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed using the lens formula.
Study the following diagram and select the correct statement about the device 'X' :

(A) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(B) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 6 cm
(C) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm
(D) Device 'X' is a convex of mirror of focal length 12 cm
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should the position of the object be relative to the mirror? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
Which kind of mirror is used in the headlights of a car? Why is it used for this purpose?
Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a real image by a converging mirror.
What type of mirror should be used as a shaving mirror?
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between the focus and centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image. What happens to the image as the object is moved away from the mirror?
Identify the device used as a spherical mirror or lens in following case, when the image formed is virtual and erect in case.
Object is placed between device and its focus, image formed is enlarged and behind it.
