Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a real image by a converging mirror.
Solution
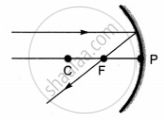
A real image is formed by a converging mirror when an object is placed anywhere between the focus and infinity, including the focus and infinity:
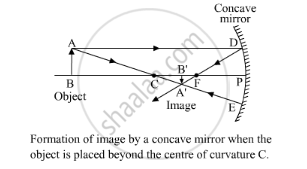
Here, P: pole, F: focus, C: centre of curvature, AB: object and A'B': image.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? Draw ray diagram for this situation also justify your answer. Show the positions of pole, principal focus and the centre of curvature in the above ray diagrams
Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a concave mirror.
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a mirror is formed on a screen placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from its pole. What is the nature of the mirror? Find its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm, find the height of its image. State whether the image formed is erect or inverted
Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a virtual image by a converging mirror.
Mark clearly the pole, focus, centre of curvature and position of object in each case.
What is the position of the image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm?
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
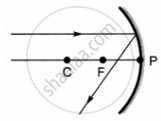
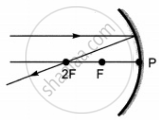
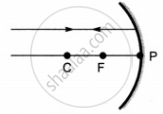
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?

 |
 |
 |
 |
| A | B | C | D |
______ mirrors magnify the object placed close to them.
Define principal focus of the concave mirror.
