Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which type of mirror is used by a dentist?
विकल्प
Plane
Convex
Concave
Both Convex and Concave
उत्तर
Concave
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a concave mirror.
Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a convex mirror.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror.
(i) Write the type of mirror in this case.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror ?
(iii) What is the nature of the image formed ?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Out of convex mirror and concave mirror, whose focus is situated behind the mirror?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
A concave mirror .......... rays of light whereas convex mirror ............ rays
If an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, where is the image formed?
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays:
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image with the help of suitable rays:
What is the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an object? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror.
Giving reasons, state the 'signs' (positive or negative) which can be given to the following:
(a) object distance (u) for a concave mirror or convex mirror
(b) image distance (v) for a concave mirror
(c) image distance (v) for a convex mirror
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Calculate the image distance.
If an object of 10 cm height is placed at a distance of 36 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm, find the position, nature and height of the image.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 4 cm and an object 2 cm tall is placed 9 cm away from it. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
An object of 5.0 cm size is placed at a distance of 20.0 cm from a converging mirror of focal length 15.0 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to get the sharp image? Also calculate the size of the image.
A concave mirror produces three times enlarged virtual image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror.
A concave mirror produces a real image 1 cm tall of an object 2.5 mm tall placed 5 cm from the mirror. Find the position of the image and the focal length of the mirror.
A man holds a spherical shaving mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm, and focal length 30 cm, at a distance of 15 cm, from his nose. Find the position of image, and calculate the magnification.
If the image formed is always virtual, the mirror can be:
(a) concave or convex
(b) concave or plane
(c) convex or plane
(d) only convex
The diagram shows a dish antenna which is used to receive television signals from a satellite. The antenna (signal detector) is fixed in front of the curved dish.
Figure
(a) What is the purpose of the dish?
(b) Should it be concave or convex?
(c) Where should the antenna be positioned to receive the strongest possible signals?
(d) Explain what change you would expect in the signals if a larger dish was used.
In the following diagram. MM' is a concave mirror and AB is an object. Draw on your answer-sheet a ray diagram to show the formation of image of this object.
A student has focused the image of a candle flame on a white screen using a concave mirror. The situation is as given below:
Length of the flame = 1.5 cm
Distance of flame from the mirror = 18 cm
If the flame is perpendicular to the principal axis of the mirror, then calculate the following:
- Distance of the image from the mirror
- Length of the image
If the distance between the mirror and the flame is reduced to 10 cm, then what would be observed on the screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer for this situation.
Choose the correct option from given alternative:
Consider the following properties of virtual images:
(A) cannot be projected on the screen
(B) are formed by both concave and convex lens
(C) are always erect
(D) are always inverted
Match the following.
| Convex mirror | Radio telescopes |
| Parobolic mirror | Rear – view mirror |
| Snell’s law | Kaleidoscope |
| Dispersion of light | sin i/sin r =μ |
| Refractive index | Rainbow |
______ is used as reflectors in torchlight.
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it?
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?

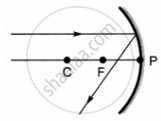 |
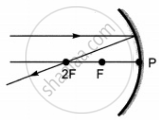 |
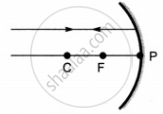 |
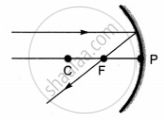 |
| A | B | C | D |
The mirror having reflection surface curved outward ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 20 cm forms an image having twice the size of object. For the virtual position of object, the position of object will be at ______.
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
In the headlights of motor vehicles, ______ mirrors are used as reflectors.
In torches, searchlights, and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed ______ of the concave mirror.
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Floodlights
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Head lamps of a car
