Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A _____________ mirror is used by a dentist.
विकल्प
concave
convex
plane
none of the above.
उत्तर
A concave mirror is used by a dentist.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
To construct ray diagrams, two rays of light are generally so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from a mirror. Choose two such rays and state the path/direction of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the position and nature of the image of an object placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification −1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror:
(i) Write the type of mirror.
(ii) What is the nature of the image formed?
(iii) How far is the object located from the mirror?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a mirror is formed on a screen placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from its pole. What is the nature of the mirror? Find its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm, find the height of its image. State whether the image formed is erect or inverted
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance from the ......... to the mirror.
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays:
Explain why, a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror gets reflected back along the same path.
Draw a ray diagram showing how a concave mirror can be used to produce a real, inverted and diminished image of an object.
Which mirror is used as a torch reflector? Draw a labelled diagram to show how a torch reflector can be used to produce a parallel beam of light. Where is the bulb placed in relation to the torch reflector?
Name the type of mirror used by dentists. How does it help?
The real image formed by a concave mirror is larger than the object when object is:
(a) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(b) at a distance less than the focal length
(c) between focus and centre of curvature
(d) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
(a) between centre of curvature and focus
(b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
(c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(d) at a distance equal to focal length
The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and highly diminished (much smaller than the object). The object must be:
(a) between pole and focus
(b) at focus
(c) at the centre of curvature
(d) at infinity
An object is 100 mm in front of a concave mirror which produces an upright (erect image). The radius of curvature of the mirror is ______.
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a concave mirror?
An object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror which produces a virtual image 4.5 cm high:
(i) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(ii) What is the position of image?
(iii) Draw a ray-diagram to show the formation of image.
A man holds a spherical shaving mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm, and focal length 30 cm, at a distance of 15 cm, from his nose. Find the position of image, and calculate the magnification.
If the object is moved further away from the mirror, what changes are there in the position and size of the image?
An object is placed at a large distance in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm. The image will be formed in front of the mirror at a distance:
(a) 20 cm
(b) 30 cm
(c) 40 cm
(d) 50 cm
The diagram shows a dish antenna which is used to receive television signals from a satellite. The antenna (signal detector) is fixed in front of the curved dish.
Figure
(a) What is the purpose of the dish?
(b) Should it be concave or convex?
(c) Where should the antenna be positioned to receive the strongest possible signals?
(d) Explain what change you would expect in the signals if a larger dish was used.
With the help of a labelled diagram, explain how a concave lens diverges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the concave lens on the diagram.
Suppose you have three concave mirrors A, B and C of focal lengths 10 cm, 15 cm and 20 cm. For each concave mirror you perform the experiment of image formation for three values of object distance of 10 cm, 20 cm and 30 cm. Giving reason answer the following:
(a) For the three object distances, identify the mirror/mirrors which will form an image of magnification – 1.
(b) Out of the three mirrors identify the mirror which would be preferred to be used for shaving purposes/makeup.
(c) For the mirror B draw ray diagram for image formation for object distances 10 cm and 20 cm.
Draw the ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
Large ______ mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it?
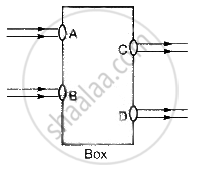
Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
In which of the following, the image of an object placed at infinity will be highly diminished and point sized?
The mirror having reflection surface curved outward ______.
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
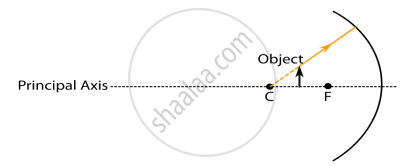
While looking at the above diagram, Nalini concluded the following.
- the image of the object will be a virtual one.
- the reflected ray will travel along the same path as the incident ray but in opposite direction.
- the image of the object will be inverted.
- this is a concave mirror and hence the focal length will be negative.
Which one of the above statements are correct?
In torches, searchlights, and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed ______ of the concave mirror.
Write the uses of the concave mirror.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Head lamps of a car
