Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
To construct ray diagrams, two rays of light are generally so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from a mirror. Choose two such rays and state the path/direction of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the position and nature of the image of an object placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm.
उत्तर
The two rays chosen to construct a ray diagram are shown in the ray diagram given below.
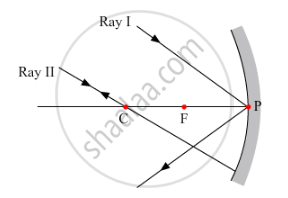
(i) Ray I:- When the ray is incident obliquely to the principle axis towards the pole of the concave mirror, the angle at which it reflects back is equal to the angle of incidence.
(ii) Ray II:- When the incident ray passes through the centre of curvature, the light, after reflection from the concave mirror, reflects back along the same path.
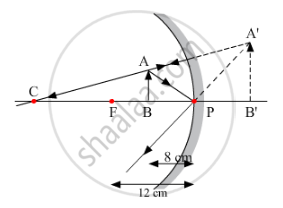
The image formed is virtual, erect and magnified. It is formed behind the mirror.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification −1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror:
(i) Write the type of mirror.
(ii) What is the nature of the image formed?
(iii) How far is the object located from the mirror?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror.
(i) Write the type of mirror in this case.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror ?
(iii) What is the nature of the image formed ?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Find the focal length of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms a real image equal in size to the object?
What kind of mirror can have a focal length of, −20 cm?
What is the position of the image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm?
A large concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 1.5 m. A person stands 10 m in front of the mirror. Where is the person's image?
How far should an object be placed from the pole of a converging mirror of focal length 20cm to form a real image of the size exactly `1/4`th the size of the object?
If the image formed is always virtual, the mirror can be:
(a) concave or convex
(b) concave or plane
(c) convex or plane
(d) only convex
Which of the following mirror is used by a dentist to examine a small cavity in a patient’s teeth?
