Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
To construct ray diagrams, two rays of light are generally so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from a mirror. Choose two such rays and state the path/direction of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the position and nature of the image of an object placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm.
उत्तर
The two rays chosen to construct a ray diagram are shown in the ray diagram given below.
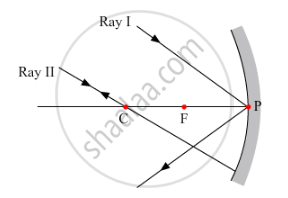
(i) Ray I:- When the ray is incident obliquely to the principle axis towards the pole of the concave mirror, the angle at which it reflects back is equal to the angle of incidence.
(ii) Ray II:- When the incident ray passes through the centre of curvature, the light, after reflection from the concave mirror, reflects back along the same path.
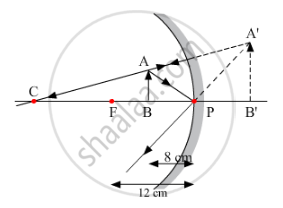
The image formed is virtual, erect and magnified. It is formed behind the mirror.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
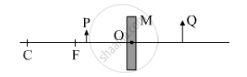
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building, about 1 km away from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen, the student should slightly move the
(a) mirror away from the screen
(b) screen away from the mirror
(c) screen towards the mirror
(d) screen towards the building
A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
between its pole and focus
Describe the nature, size and position of the image formed in each case.
State one use of concave mirror bases on the formation of image as in case (i) above.
The angle of incidence for of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror is:
(a) 45°
(b) 90°
(c) 0°
(d) 180°
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
State two characteristics of the image formed.
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
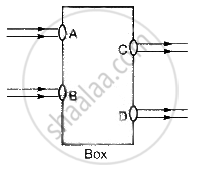
Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
A concave mirror produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed ______.
