Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
उत्तर १
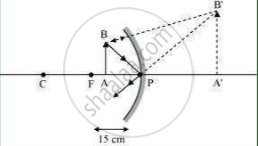
The range of the distance of the object = 0 to 15 cm from the pole of the mirror.
The nature of the image = virtual, erect, and larger than the object.
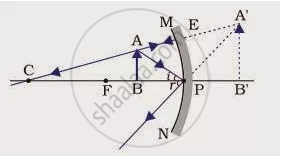
उत्तर २
Range of object distance = 0 cm to15 cm
A concave mirror gives an erect image when an object is placed between its pole (P) and the principal focus (F).
Hence, to obtain an erect image of an object from a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm, the object must be placed anywhere between the pole and the focus. The image formed will be virtual, erect, and magnified in nature, as shown in the given figure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
"A concave mirror of focal length 15 cm can form a magnified, erect as well as inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror in both the cases for obtaining the images.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
Which type of mirror is used by a dentist?
Find the focal length of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Parallel rays of light are reflected by a concave mirror to a point called the ..........
ill in the following blank with suitable word:
For a convex mirror, parallel rays of light appear to diverge from a point called the ......... .
Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a virtual image by a converging mirror.
Mark clearly the pole, focus, centre of curvature and position of object in each case.
Name the type of mirror used by dentists. How does it help?
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a concave mirror?
If an object of 10 cm height is placed at a distance of 36 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm, find the position, nature and height of the image.
How far should an object be placed from the pole of a converging mirror of focal length 20cm to form a real image of the size exactly `1/4`th the size of the object?
Which of the following are concave mirrors and which convex mirrors?
The diagram shows a dish antenna which is used to receive television signals from a satellite. The antenna (signal detector) is fixed in front of the curved dish.
Figure
(a) What is the purpose of the dish?
(b) Should it be concave or convex?
(c) Where should the antenna be positioned to receive the strongest possible signals?
(d) Explain what change you would expect in the signals if a larger dish was used.
How can a concave mirror be used to obtain a virtual image of an object? Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
A student has to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of angle of incidence.
(a) Write two important precautions for this experiment.
(b) List two conclusions the student will draw based on his experiment.
The mirror used by the ophthalmologist to examine the eye is _______.
Give any two applications of a concave and convex mirror.
Write the uses of the concave mirror.
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Shaving mirror
