Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and highly diminished (much smaller than the object). The object must be:
(a) between pole and focus
(b) at focus
(c) at the centre of curvature
(d) at infinity
उत्तर
At infinity
The reason being, the image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and highly diminished (much smaller than the object). Therefore, the object must be at infinity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
To determine the approximate value of the focal length of a given concave mirror, you focus the image of a distant object formed by the mirror on a screen. The image obtained on the serene, as compared to the object is always:
(a) Laterally inverted and diminished
(b) Inverted and diminished
(c) Erect and diminished
(d) Erect and highly diminished
Which mirror is used as a torch reflector? Draw a labelled diagram to show how a torch reflector can be used to produce a parallel beam of light. Where is the bulb placed in relation to the torch reflector?
Write down a formula for the magnification produced by a concave mirror.
in terms of height of object and height of image
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Calculate the image distance.
What type of mirror should be used as a shaving mirror?
The mirror which can form a magnified image of an object is:
(a) convex mirror
(b) plane mirror
(c) concave mirror
(d) both convex and concave mirror
Complete the following diagrams in figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2 if F is the focus and C is the centre of curvature.
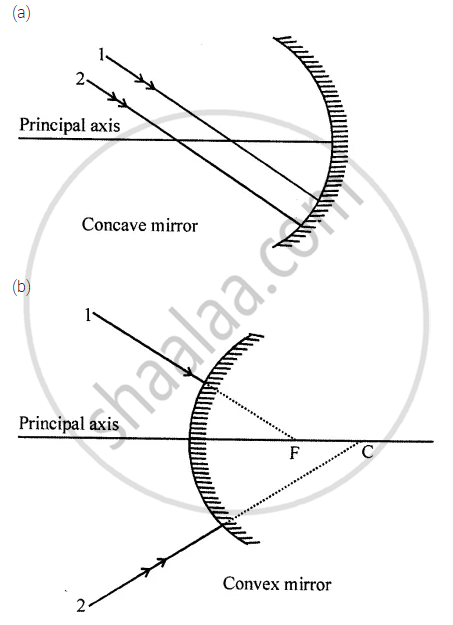
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image. What happens to the image as the object is moved away from the mirror?
State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement.
When an object is at the centre of curvature of concave mirror the image formed will be virtual and erect.
An image formed by a lens is erect. Such an image could be formed by a
