Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
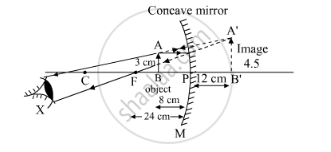
An object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror which produces a virtual image 4.5 cm high:
(i) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(ii) What is the position of image?
(iii) Draw a ray-diagram to show the formation of image.
उत्तर
Distance of the object from the mirror 'u' = -8 cm
Height of the object 'ho' = 3 cm
Height of the image 'hi' = 4.5 cm
We have to find the focal length of the mirror 'f' and distance of the image 'v'.
Using the magnification formula, we get
`m=h_i/h-o=-v/u`
`m4.5/3=(-v)/(-8)`
`v=4.5xx8/3=12`cm
Therefore, the distance of the image 'v' is 12 cm behind the mirror.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A concave mirror produces three times magnified image on a screen. If the object is placed 20 cm in front of the mirror, how far is the screen from the object.
Which type of mirror is used by a dentist?
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
State two characteristics of the image formed.
If the object is moved further away from the mirror, what changes are there in the position and size of the image?
An object is placed at a large distance in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm. The image will be formed in front of the mirror at a distance:
(a) 20 cm
(b) 30 cm
(c) 40 cm
(d) 50 cm
The diagram shows a dish antenna which is used to receive television signals from a satellite. The antenna (signal detector) is fixed in front of the curved dish.
Figure
(a) What is the purpose of the dish?
(b) Should it be concave or convex?
(c) Where should the antenna be positioned to receive the strongest possible signals?
(d) Explain what change you would expect in the signals if a larger dish was used.
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
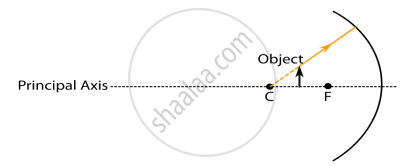
While looking at the above diagram, Nalini concluded the following.
- the image of the object will be a virtual one.
- the reflected ray will travel along the same path as the incident ray but in opposite direction.
- the image of the object will be inverted.
- this is a concave mirror and hence the focal length will be negative.
Which one of the above statements are correct?
A student wants to obtain an erect image of an object using a concave mirror of 10 cm focal length. What will be the distance of the object from mirror?
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
