Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the positions of the source of light with respect to a concave mirror in Projector lamp.
उत्तर
In a projector lamp, the light source is at the centre of the curvature of a concave mirror, which produces an image of the shape of the object itself.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a concave mirror.
Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
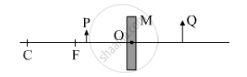
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
List four characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors.
We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a mirror is formed on a screen placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from its pole. What is the nature of the mirror? Find its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm, find the height of its image. State whether the image formed is erect or inverted
Which type of mirror is used by a dentist?
Find the focal length of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance from the ......... to the mirror.
Draw diagram to represent the action of a concave mirror on a beam of parallel light rays. Mark on this diagram principal axis, focus F, centre of curvature C, pole P and focal length f, of the concave mirror.
Which kind of mirror is used in the headlights of a car? Why is it used for this purpose?
With the help of a ray diagram, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
If an object is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm, discuss the nature of the image formed by drawing the ray diagram.
With the help of a labelled ray diagram, describe how a converging mirror can be used to give an enlarged upright image of an object.
Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a real image by a converging mirror.
Which type of mirror is used in a solar furnace? Support your answer with reason.
The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
(a) between centre of curvature and focus
(b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
(c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(d) at a distance equal to focal length
An object is placed at the following distances from a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm, turn by turn:
(a) 35 cm
(b) 30 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 10 cm
Which position of the object will produce:
(i) a magnified real image?
(ii) a magnified virtual image?
(iii) a diminished real image?
(iv) an image of same size as the object?
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a concave mirror?
What is the position of the image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm?
If an object of 10 cm height is placed at a distance of 36 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm, find the position, nature and height of the image.
An object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror which produces a virtual image 4.5 cm high:
(i) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(ii) What is the position of image?
(iii) Draw a ray-diagram to show the formation of image.
An object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a converging mirror of focal length 20 cm. Find the position, nature, and size of the image formed.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 4 cm and an object 2 cm tall is placed 9 cm away from it. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
If the object is moved further away from the mirror, what changes are there in the position and size of the image?
What would your image look like if you stood close to a large:
concave mirror?
Which of the following are concave mirrors and which convex mirrors?
Shaving mirrors, Car headlight mirror, Searchlight mirror, Driving mirror, Dentist's inspection mirror, Touch mirror, Staircase mirror in a double-decker bus, Make-up mirror, Solar furnace mirror, Satellite TV dish, Shop security mirror.
An object is placed 15 cm from (a) a converging mirror, and (b) a diverging mirror, of radius of curvature 20 cm. Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
Why does a beam of light when it enters glass at an angle? Why does it not bend if it inters the glass at right angles?
If the radius of curvature of a concave mirror is 20 cm, its focal length is:
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
How can a concave mirror be used to obtain a virtual image of an object? Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
In the following diagram. MM' is a concave mirror and AB is an object. Draw on your answer-sheet a ray diagram to show the formation of image of this object.
A student determines the focal length of a device 'X' by focusing the image of a distant object on a screen placed 20 cm from the device on the same side as the object. The device 'X' is
(a) Concave lens of focal length 10 cm
(b) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm
(c) Concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
(d) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm
Draw the ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
A student has to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of angle of incidence.
(a) Write two important precautions for this experiment.
(b) List two conclusions the student will draw based on his experiment.
Why are concave mirrors used in solar devices?
Why does obtaining the image of the sun on paper with the help of a concave mirror burn the paper?
The mirror used by the ophthalmologist to examine the eye is _______.
The radius of curvature of a concave mirror whose focal length is 5cm is ______
Large ______ mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
Concave mirrors are used by dentists to examine teeth. Why?
A concave mirror of focal length 20 cm forms an image having twice the size of object. For the virtual position of object, the position of object will be at ______.
Which of the following mirror is used by a dentist to examine a small cavity in a patient’s teeth?
You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
An erect and enlarged image can be formed by
In the headlights of motor vehicles, ______ mirrors are used as reflectors.
In torches, searchlights, and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed ______ of the concave mirror.
A student wants to obtain an erect image of an object using a concave mirror of 10 cm focal length. What will be the distance of the object from mirror?
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Floodlights
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Head lamps of a car
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Shaving mirror
