Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the positions of the source of light with respect to a concave mirror in Projector lamp.
उत्तर
In a projector lamp, the light source is at the centre of the curvature of a concave mirror, which produces an image of the shape of the object itself.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the refracted ray in each of the following cases:-
A ray of light incident on a concave lens is
(i) passing through its optical centre.
(ii) parallel to its principal axis.
(iii) directed towards its principal focus.
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? Draw ray diagram for this situation also justify your answer. Show the positions of pole, principal focus and the centre of curvature in the above ray diagrams
To determine the approximate value of the focal length of a given concave mirror, you focus the image of a distant object formed by the mirror on a screen. The image obtained on the serene, as compared to the object is always:
(a) Laterally inverted and diminished
(b) Inverted and diminished
(c) Erect and diminished
(d) Erect and highly diminished
List four characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors.
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.
A student has obtained the image of a distant object with a concave mirror to determine its focal length. If he has selected a well-illuminated red building as object, which of the following correctly describes the features of the image formed?
(A) Virtual, inverted and diminished image in red shade
(B) Real, erect and diminished image in pink shade
(C) Real, inverted and diminished image in red shade
(D) Virtual, erect and enlarged image in red shade
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of the school laboratory by using a mirror.
(a) Which type of mirror should he use and why?
(b) At what distance, in terms of focal length 'f' of the mirror, should he place the candle flame to get the magnified image on the wall?
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case.
(d) Can he use this mirror to project a diminished image of the candle flame on the same wall? State 'how' if your answer is 'yes' and 'why not' if your answer is 'no.'
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror making an angle of 90° with the mirror surface. The angle of reflection for this ray of light will be:
(a) 45°
(b) 90°
(c) 0°
(d) 60°
Out of convex mirror and concave mirror, whose focus is situated behind the mirror?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
A concave mirror .......... rays of light whereas convex mirror ............ rays
Draw diagram to represent the action of a concave mirror on a beam of parallel light rays. Mark on this diagram principal axis, focus F, centre of curvature C, pole P and focal length f, of the concave mirror.
Copy this figure in your answer book and show the direction of the light ray after reflection:
Described with the help of a diagram, the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
State where an object must be placed so that the image formed by a concave mirror is:
(b) at infinity.
(c) the same size as the object.
The real image formed by a concave mirror is larger than the object when object is:
(a) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(b) at a distance less than the focal length
(c) between focus and centre of curvature
(d) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
(a) between centre of curvature and focus
(b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
(c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(d) at a distance equal to focal length
The focal length of a small concave mirror is 2.5 cm. In order to use this concave mirror as a dentist's mirror, the distance of tooth from the mirror should be:
(a) 2.5 cm
(b) 1.5 cm
(c) 4.5 cm
(d) 3.5 cm
What is the position of the image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm?
At what distance from a concave mirror focal length 10 cm should an object 2 cm long be placed in order to get an erect image 6 cm tall?
An object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror which produces a virtual image 4.5 cm high:
(i) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(ii) What is the position of image?
(iii) Draw a ray-diagram to show the formation of image.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 4 cm and an object 2 cm tall is placed 9 cm away from it. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
A concave mirror produces three times enlarged virtual image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror.
An object is 24 cm away from a concave mirror and its image is 16 cm from the mirror. Find the focal length and radius of curvature of the mirror, and the magnification of the image.
What type of image/images are formed by:
a convex mirror?
What type of mirror should be used as a shaving mirror?
What would your image look like if you stood close to a large:
concave mirror?
If the image formed is always virtual, the mirror can be:
(a) concave or convex
(b) concave or plane
(c) convex or plane
(d) only convex
The mirror which can form a magnified image of an object is:
(a) convex mirror
(b) plane mirror
(c) concave mirror
(d) both convex and concave mirror
A real image of an object is to be obtained. The mirror required for this purpose is:
(a) convex
(b) concave
(c) plane
(d) either convex or concave
Name the lens which can concentrate sun's rays to a point and burn a hole in a piece of paper.
A convex mirror is used as a shaving mirror.
Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is ............. its focal length.
The image formed by a concave mirror is of the same size as the object, if the object is placed
In the following diagram. MM' is a concave mirror and AB is an object. Draw on your answer-sheet a ray diagram to show the formation of image of this object.
In which equipment/s do you find ___________________
Study the following ray diagram and list two mistakes committed by the student while tracing it. Rectify these mistakes by drawing the correct ray diagram to show the real position and size of the image corresponding to the position of the object AB.

______ is used as reflectors in torchlight.
Concave mirrors are used by dentists to examine teeth. Why?
A 10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror. A 5 mm long image of the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The focal length of this mirror is ______.
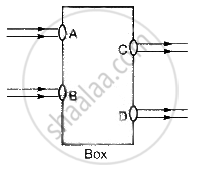
Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
The image formed by concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object. The position of object should be ______.
Which of the following mirror is used by a dentist to examine a small cavity in a patient’s teeth?
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
You are provided with a convex mirror, a concave mirror, a convex lens and a concave lens. You can get an inverted image from
In the headlights of motor vehicles, ______ mirrors are used as reflectors.
______ mirrors make things look larger when objects are placed close to them.
A student wants to obtain an erect image of an object using a concave mirror of 10 cm focal length. What will be the distance of the object from mirror?
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
