Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
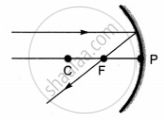
Describe the positions of the source of light with respect to a concave mirror in Floodlight.
उत्तर
In a floodlight, the light source is slightly beyond the radius of curvature, which gives us the right light.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the refracted ray in each of the following cases:-
A ray of light incident on a concave lens is
(i) passing through its optical centre.
(ii) parallel to its principal axis.
(iii) directed towards its principal focus.
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building, about 1 km away from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen, the student should slightly move the
(a) mirror away from the screen
(b) screen away from the mirror
(c) screen towards the mirror
(d) screen towards the building
List four characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should the position of the object be relative to the mirror? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror.
(i) Write the type of mirror in this case.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror ?
(iii) What is the nature of the image formed ?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
A concave mirror produces three times magnified image on a screen. If the object is placed 20 cm in front of the mirror, how far is the screen from the object.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a mirror is formed on a screen placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from its pole. What is the nature of the mirror? Find its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm, find the height of its image. State whether the image formed is erect or inverted
The angle between an incident ray and the plane mirror is 30°. The total angle between the incident ray and reflected ray will be:
(a) 30°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 120°
Define (i) principal focus of a concave mirror, and (ii) focal length of a concave mirror.
For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms a real image equal in size to the object?
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays:
Which kind of mirror is used in the headlights of a car? Why is it used for this purpose?
State where an object must be placed so that the image formed by a concave mirror is:
(b) at infinity.
(c) the same size as the object.
Explain why, concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors.
The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and highly diminished (much smaller than the object). The object must be:
(a) between pole and focus
(b) at focus
(c) at the centre of curvature
(d) at infinity
Describe the nature of image formed when the object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Calculate the image distance.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 4 cm and an object 2 cm tall is placed 9 cm away from it. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
How far should an object be placed from the pole of a converging mirror of focal length 20cm to form a real image of the size exactly `1/4`th the size of the object?
A man holds a spherical shaving mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm, and focal length 30 cm, at a distance of 15 cm, from his nose. Find the position of image, and calculate the magnification.
At what distance from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm should an object be placed so that:
its real image is formed 20 cm from the mirror?
What type of mirror should be used as a shaving mirror?
Which of the following are concave mirrors and which convex mirrors?
Which of the following are concave mirrors and which convex mirrors?
Shaving mirrors, Car headlight mirror, Searchlight mirror, Driving mirror, Dentist's inspection mirror, Touch mirror, Staircase mirror in a double-decker bus, Make-up mirror, Solar furnace mirror, Satellite TV dish, Shop security mirror.
A concave mirror cannot be used as:
(a) a magnifying mirror
(b) a torch reflector
(c) a dentist's mirror
(d) a real view mirror
If the radius of curvature of a concave mirror is 20 cm, its focal length is:
In the following diagram. MM' is a concave mirror and AB is an object. Draw on your answer-sheet a ray diagram to show the formation of image of this object.
Suppose you have three concave mirrors A, B and C of focal lengths 10 cm, 15 cm and 20 cm. For each concave mirror you perform the experiment of image formation for three values of object distance of 10 cm, 20 cm and 30 cm. Giving reason answer the following:
(a) For the three object distances, identify the mirror/mirrors which will form an image of magnification – 1.
(b) Out of the three mirrors identify the mirror which would be preferred to be used for shaving purposes/makeup.
(c) For the mirror B draw ray diagram for image formation for object distances 10 cm and 20 cm.
A student determines the focal length of a device 'X' by focusing the image of a distant object on a screen placed 20 cm from the device on the same side as the object. The device 'X' is
(a) Concave lens of focal length 10 cm
(b) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm
(c) Concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
(d) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm
A student has to determine the focal length of a concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant object on a screen. For getting best result he should focus
(A) a distant tree or an electric pole
(B) a well-illuminated distant building
(C) well-lit grills of the nearest window
(D) a burning candle laced at the distant edge of the laboratory table
A student has to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of angle of incidence.
(a) Write two important precautions for this experiment.
(b) List two conclusions the student will draw based on his experiment.
In which equipment/s do you find ___________________
Answer the following question:
An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Use the lens formula to determine the distance of the image from the lens.
(ii) List four characteristics of the image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) in this case.
(iii) Draw a labelled diagram to justify your answer of the part (ii)
The mirror used by the ophthalmologist to examine the eye is _______.
Explain the images formed by a concave mirror.
State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement.
When an object is at the centre of curvature of concave mirror the image formed will be virtual and erect.
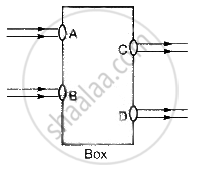
Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
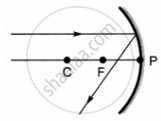
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?

 |
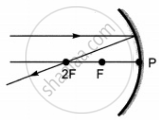 |
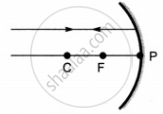 |
 |
| A | B | C | D |
A concave mirror produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed ______.
For a real object, which of the following can produce a real image?
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
An erect and enlarged image can be formed by
You are provided with a convex mirror, a concave mirror, a convex lens and a concave lens. You can get an inverted image from
State whether the following statement is True or False
The sides of an object and its image formed by a concave mirror are always interchanged.
______ mirrors magnify the object placed close to them.
Define principal focus of the concave mirror.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Shaving mirror
