Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should the position of the object be relative to the mirror? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
उत्तर
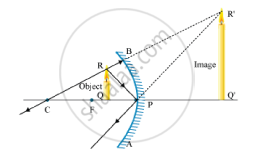
When the object is located between the focus (F) and the pole (P) of the mirror, the image is formed behind the mirror; this image is virtual, erect and large.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Study the following diagram and select the correct statement about the device 'X' :

(A) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(B) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 6 cm
(C) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm
(D) Device 'X' is a convex of mirror of focal length 12 cm
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Headlights of a car
Support your answer with reason.
For what position of an object, a real and diminished image is formed by a concave mirror?
Which type of mirror is used in a solar furnace? Support your answer with reason.
between its pole and focus
Describe the nature, size and position of the image formed in each case.
State one use of concave mirror bases on the formation of image as in case (i) above.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 4 cm and an object 2 cm tall is placed 9 cm away from it. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
At what distance from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm should an object be placed so that:
its real image is formed 20 cm from the mirror?
The diagram shows a dish antenna which is used to receive television signals from a satellite. The antenna (signal detector) is fixed in front of the curved dish.
Figure
(a) What is the purpose of the dish?
(b) Should it be concave or convex?
(c) Where should the antenna be positioned to receive the strongest possible signals?
(d) Explain what change you would expect in the signals if a larger dish was used.
Complete the following diagrams in figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2 if F is the focus and C is the centre of curvature.
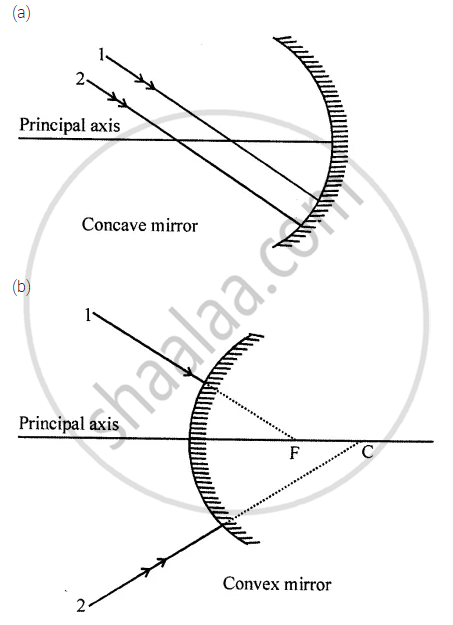
Name the mirror(s) that can give (i) an erect and enlarged image, (ii) same sized, inverted image
