Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should the position of the object be relative to the mirror? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
उत्तर
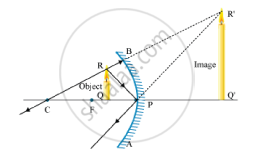
When the object is located between the focus (F) and the pole (P) of the mirror, the image is formed behind the mirror; this image is virtual, erect and large.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the refracted ray in each of the following cases:-
A ray of light incident on a concave lens is
(i) passing through its optical centre.
(ii) parallel to its principal axis.
(iii) directed towards its principal focus.
To determine the approximate value of the focal length of a given concave mirror, you focus the image of a distant object formed by the mirror on a screen. The image obtained on the serene, as compared to the object is always:
(a) Laterally inverted and diminished
(b) Inverted and diminished
(c) Erect and diminished
(d) Erect and highly diminished
Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a convex mirror.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Draw ray-diagrams to show the formation of images when the object is places in front of a concave mirror (converging mirror):
(i) between its pole and focus
(ii) between its centre of curvature and focus
Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is ............. its focal length.
To find the focal length of a concave mirror Rahul focuses a distant object with this mirror. The chosen object should be
(1) a tree
(2) a building
(3) a window
(4) the sun
Study the following ray diagram and list two mistakes committed by the student while tracing it. Rectify these mistakes by drawing the correct ray diagram to show the real position and size of the image corresponding to the position of the object AB.

Pick out the concave and convex mirrors from the following and tabulate them.
Rear-view mirror, Dentist’s mirror, Torchlight mirror, Mirrors in shopping malls, Make-up mirror.
