Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw ray-diagrams to show the formation of images when the object is places in front of a concave mirror (converging mirror):
(i) between its pole and focus
(ii) between its centre of curvature and focus
उत्तर
When an object is placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is virtual, erect, magnified and behind the mirror. This is illustrated as follows:
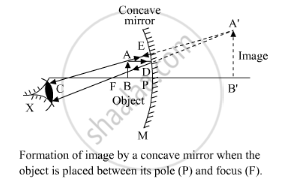
Here, the image A'B' of the object AB, placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror, is virtual and erect.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If an object is at infinity (very large distance) in front of a concave mirror, where is the image formed?
What is the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an object? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror.
An object is 100 mm in front of a concave mirror which produces an upright (erect image). The radius of curvature of the mirror is ______.
Name the mirror which can give:
an erect and enlarged image of an object.
What type of mirror should be used as a shaving mirror?
An object is placed 15 cm from (a) a converging mirror, and (b) a diverging mirror, of radius of curvature 20 cm. Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
Draw and complete the following diagrams to show what happens to the beams of light as they enter the glass block and then leave it:
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Explain the images formed by a concave mirror.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Head lamps of a car
