Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw ray-diagrams to show the formation of images when the object is places in front of a concave mirror (converging mirror):
(i) between its pole and focus
(ii) between its centre of curvature and focus
उत्तर
When an object is placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is virtual, erect, magnified and behind the mirror. This is illustrated as follows:
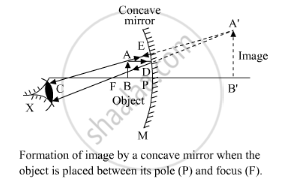
Here, the image A'B' of the object AB, placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror, is virtual and erect.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
Three students A, B and C focussed a distant building on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. To determine focal length of the concave mirror they measured the distances as given below:
Student A : From mirror to the screen
Student B : From building to the screen
Student C : From building to the mirror
Who measured the focal length correctly ;
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror.
Which kind of mirror is used in the headlights of a car? Why is it used for this purpose?
A bright object 50 mm high stands on the axis of a concave mirror of focal length 100 mm and at a distance of 300 mm from the concave mirror. How big will the image be?
What type of image/images are formed by:
a convex mirror?
Which of the following are concave mirrors and which convex mirrors?
Shaving mirrors, Car headlight mirror, Searchlight mirror, Driving mirror, Dentist's inspection mirror, Touch mirror, Staircase mirror in a double-decker bus, Make-up mirror, Solar furnace mirror, Satellite TV dish, Shop security mirror.
The mirror having reflection surface curved outward ______.
The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object, the position of the object should be ______.
