Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
पर्याय
Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature
At the centre of curvature
Beyond the centre of curvature
Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
उत्तर
Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Explanation:
For a virtual, erect and larger image, the object must lie between the pole of the mirror and its focus.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
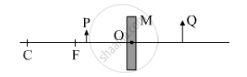
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should the position of the object be relative to the mirror? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Headlights of a car
Support your answer with reason.
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a concave mirror?
According to New Cartesian Sign Convention:
(a) focal length of concave mirror is positive and that of convex mirror is negative
(b) focal length of both concave and convex mirrors is positive
(c) focal length of both concave and convex mirrors is negative
(d) focal length of concave mirror is negative and that of convex mirror is positive
A converging mirror forms a real image of height 4 cm of an object of height 1 cm placed 20 cm away from the mirror:
(i) Calculate the image distance.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror?
An object is placed just outside the principal focus of concave mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show how the image is formed, and describe its size, position and nature.
An object is placed at a large distance in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm. The image will be formed in front of the mirror at a distance:
(a) 20 cm
(b) 30 cm
(c) 40 cm
(d) 50 cm
With the help of a labelled diagram, explain how a concave lens diverges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the concave lens on the diagram.
Suppose you have three concave mirrors A, B and C of focal lengths 10 cm, 15 cm and 20 cm. For each concave mirror you perform the experiment of image formation for three values of object distance of 10 cm, 20 cm and 30 cm. Giving reason answer the following:
(a) For the three object distances, identify the mirror/mirrors which will form an image of magnification – 1.
(b) Out of the three mirrors identify the mirror which would be preferred to be used for shaving purposes/makeup.
(c) For the mirror B draw ray diagram for image formation for object distances 10 cm and 20 cm.
A student obtained a sharp image of the grills of a window on a screen using a concave mirror. His teacher remarked that for getting better results a well lit distant object (preferably the sun) should be focussed on the screen. What should be done for this purpose?
(A) Move the screen slightly away from the mirror
(B) Move the mirror slightly towards the screen
(C) Move the screen and the mirror away from the object
(D) Move the screen and the mirror towards the object
A _____________ mirror is used by a dentist.
Match the following.
| Convex mirror | Radio telescopes |
| Parobolic mirror | Rear – view mirror |
| Snell’s law | Kaleidoscope |
| Dispersion of light | sin i/sin r =μ |
| Refractive index | Rainbow |
The image formed by concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object. The position of object should be ______.
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
An image formed by a lens is erect. Such an image could be formed by a
______ mirrors magnify the object placed close to them.
