Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
उत्तर
OBJECT PLACED BEYOND C: Image is formed :
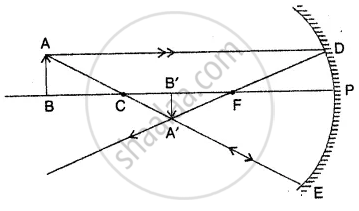
A real, inverted and smaller image is formed between the centre of curvature and focus
Position: between C and F.
Size smaller than an object.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
"A concave mirror of focal length 15 cm can form a magnified, erect as well as inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror in both the cases for obtaining the images.
Study the following diagram and select the correct statement about the device 'X' :

(A) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(B) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 6 cm
(C) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm
(D) Device 'X' is a convex of mirror of focal length 12 cm
The angle between an incident ray and the plane mirror is 30°. The total angle between the incident ray and reflected ray will be:
(a) 30°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 120°
between its pole and focus
Describe the nature, size and position of the image formed in each case.
State one use of concave mirror bases on the formation of image as in case (i) above.
An object is 24 cm away from a concave mirror and its image is 16 cm from the mirror. Find the focal length and radius of curvature of the mirror, and the magnification of the image.
An object is placed 15 cm from (a) a converging mirror, and (b) a diverging mirror, of radius of curvature 20 cm. Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
To construct ray diagram we use two light rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection. Use these rays to locate the image of an object placed between centre of curvature and focus of a concave mirror.
List four characteristics of the image formed by a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm when the object is placed in front of it at a distance of 20 cm from its pole.
Define principal focus of the concave mirror.
