Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw diagram to represent the action of a concave mirror on a beam of parallel light rays. Mark on this diagram principal axis, focus F, centre of curvature C, pole P and focal length f, of the concave mirror.
उत्तर
Ray Diagram-
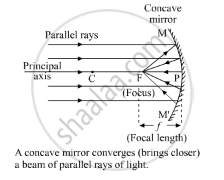
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
Name the mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image.
If an object is at infinity (very large distance) in front of a concave mirror, where is the image formed?
What is the position of the image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm?
The mirror used by a dentist to examine the teeth of a person is:
(d) any one of the above
(a) convex
(b) concave
(c) plane
(d) any one of the above
How can a concave mirror be used to obtain a virtual image of an object? Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
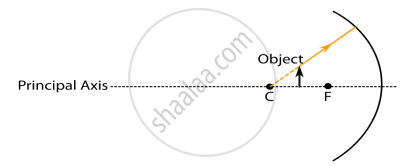
While looking at the above diagram, Nalini concluded the following.
- the image of the object will be a virtual one.
- the reflected ray will travel along the same path as the incident ray but in opposite direction.
- the image of the object will be inverted.
- this is a concave mirror and hence the focal length will be negative.
Which one of the above statements are correct?
You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
