Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
Solution
Magnification produced by a spherical mirror is given by the relation,
`m=h_1/h_0=-u/v`
Let the height of the object, `h_0=h`
Then, height of the image, `h_1=-3h `(image formed is real)
`-3h/h=-v/u`
`v/u=3`
Object distance, u = –10 cm
v = 3 × (–10) = –30 cm
Here, the negative sign indicates that an inverted image is formed at a distance of
30 cm in front of the given concave mirror.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the refracted ray in each of the following cases:-
A ray of light incident on a concave lens is
(i) passing through its optical centre.
(ii) parallel to its principal axis.
(iii) directed towards its principal focus.
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
What should be the range of distance of an object placed in front of the mirror?
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a mirror is formed on a screen placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from its pole. What is the nature of the mirror? Find its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm, find the height of its image. State whether the image formed is erect or inverted
For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms a real image equal in size to the object?
If an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, where is the image formed?
With the help of a ray diagram, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
Draw ray-diagrams to show the formation of images when the object is places in front of a concave mirror (converging mirror):
(i) between its pole and focus
(ii) between its centre of curvature and focus
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a convex mirror?
What kind of mirror can have a focal length of, −20 cm?
According to New Cartesian Sign Convention:
(a) focal length of concave mirror is positive and that of convex mirror is negative
(b) focal length of both concave and convex mirrors is positive
(c) focal length of both concave and convex mirrors is negative
(d) focal length of concave mirror is negative and that of convex mirror is positive
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Calculate the image distance.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 4 cm and an object 2 cm tall is placed 9 cm away from it. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
An object is placed at a large distance in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm. The image will be formed in front of the mirror at a distance:
(a) 20 cm
(b) 30 cm
(c) 40 cm
(d) 50 cm
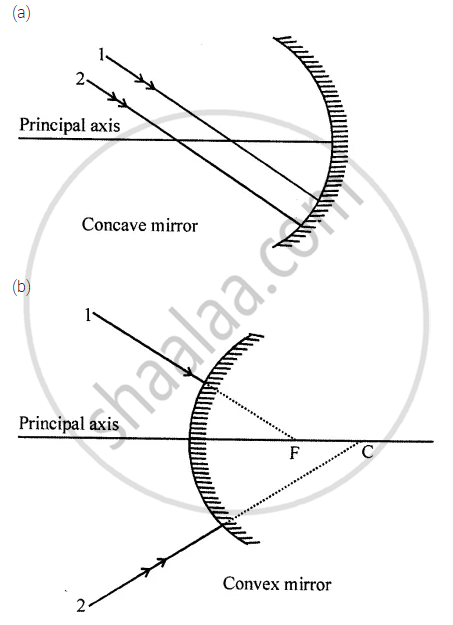
Complete the following diagrams in figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2 if F is the focus and C is the centre of curvature.
A student obtained a sharp inverted image of a distant tree on a screen placed in front of the concave mirror. He then removed the screen and tried to look into the mirror. He would now see
(A) a very blurred image on the wall opposite to the mirror
(B) an erect and magnified image of the tree in the mirror
(C) no image as the screen has been removed
(D) a highly diminished inverted image of the tree at the focus of the mirror.
The mirror having reflecting surface curved inwards ______.
______ mirrors magnify the object placed close to them.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Floodlights
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Shaving mirror
