Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Solution
Radius of curvature, R = 32 cm
Radius of curvature = 2 × Focal length (f)
f = `R/2`
f = `32/2`
f = 16
Hence, the focal length of the given convex mirror is 16 cm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Describe with a suitable diagram, how a convex mirror diverges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus and centre of curvature of concave mirror in this diagram.
Which type of mirror has:
positive focal length?
Which type of mirror has:
negative focal length?
Name the mirror which can give:
an erect and diminished image of an object.
Where would the image be formed by a convex mirror if the object is placed:
at infinity?
Draw labelled ray-diagrams to show the formation of image in both the case.
Give two uses of a convex mirror. Explain why you would choose convex mirror for these uses.
If a driver has one convex and one plane rear-view mirror, how would the images in each mirror appear different?
The image formed by a spherical mirror is virtual. The mirror will be:
(a) concave
(b) convex
(c) either concave or convex
(d) metallic
Two big mirrors A and B are fitted side by side on a wall. A man is standing at such a distance from the wall that he can see the erect image of his face in both the mirrors. When the man starts walking towards the mirrors, he find that the size of his face in mirror A goes on increasing but that in mirror B remains the same.
(a) mirror A is concave and mirror B is convex
(b) mirror A is plane and mirror B is concave
(c) mirror A is concave and mirror B is plane
(d) mirror A is convex and mirror B is concave
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 5 cm.
(a) Draw a ray-diagram showing the formation image
(b) State two characteristics of the image formed
(c) Calculate the distance of the image from mirror.
Draw a diagram to represent a convex mirror. On this diagram mark principal axis, principal focus F and the centre of C if the focal length of convex mirror is 3 cm.
An object 1 cm tall is placed 30 cm in front of a convex mirror of focal length 20 cm. Find the size and position of the image formed by the convex mirror.
Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed:
between F1 and the optical centre O of the lens.
Which of the above two cases shows the use of convex lens as a magnifying glass? Give reasons for your choice.
At the point of incidence, a line drawn at right angles to the surface, separating the two media, is called the normal.
A ............ mirror always forms a virtual image.
The image formed by a convex mirror is
The diagram given below in fig shows a ray of light AO falling on a surface separating two media. Draw the refracted ray in each, case.
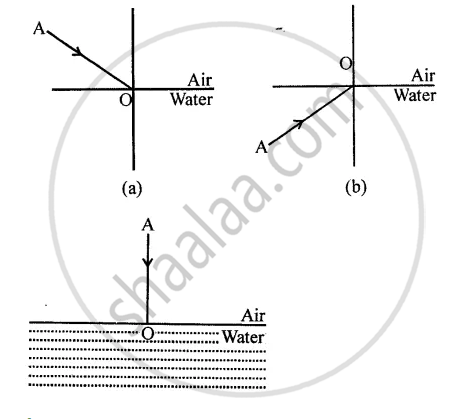
List four properties of the image formed by a convex mirror when object is placed between focus and pole of the mirror.
If the object is at infinity in front of a convex mirror the image is formed at infinity.
