Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
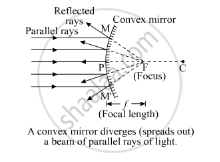
Describe with a suitable diagram, how a convex mirror diverges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus and centre of curvature of concave mirror in this diagram.
Solution
When a parallel beam of light, also parallel to the principle axis, is incident on a convex mirror, it will reflect from the mirror, and the reflected rays will appear to come from a point which is called the focus (F) of the convex mirror. So, a convex mirror has a virtual focus.
Ray diagram- A convex mirror diverges a parallel beam of light rays.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be ______.
Which mirror always produces a virtual, erect and diminished image of an object?
An object placed 20 cm in front of a mirror is found to have an image 15 cm (a) in front of it, (b) behind the mirror. Find the focal length of the mirror and the kind of mirror in each case.
An object is placed well outside the principal focus of a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram to show how the image is formed, and say whether the image is real or virtual.
Light travels in the same straight line path while passing through different media.
Write true or false
The focal length of a convex mirror is equal to its radius of curvature.
A driver uses a convex mirror as a rearview mirror. Explain the reason with the help of a ray diagram.
Nature of the images formed by a convex mirror is _______.
Numerical problem.
A concave mirror produces three times magnified real image of an object placed at 7 cm in front of it. Where is the image located? (Ans: 21 cm in front of the mirror)
Identify the device used as a spherical mirror or lens in following case, when the image formed is virtual and erect in case.
Object is placed between infinity and device, image formed is diminished and between pole and focus, behind it.
