Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain with a suitable diagram, how a concave mirror converges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus and centre of curvature of concave mirror in this diagram.
Solution
When a parallel beam of light, also parallel to the principle axis, is incident on a concave mirror, it reflects from the mirror and meets at a point called the focus (F) of the concave mirror. So, a concave mirror has a real focus.
Ray diagram- A concave mirror converges a parallel beam of light rays.
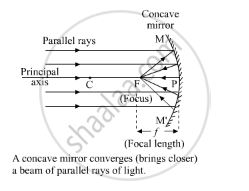
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object is placed at a distance of 40 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror.
Find the nature and focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is +24 cm.
A mirror forms an image which is 30 cm from an object and twice its height.
(a) Where must the mirror be situated?
(b) What is the radius of curvature?
(c) Is the mirror convex or concave?
What would your image look like if you stood close to a large:
convex mirror?
Draw diagram to show how a convex mirror can be used to give a large field of view.
An arrow 2.5 cm high is placed at a distance of 25 cm from a diverging mirror of focal length 20 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
A shop security mirror 5.0 m from certain items displayed in the shop produces on-tenth magnification.
What is the type of mirror?
Write true or false
At the point of incidence, a line drawn at right angles to the surface, separating the two media, is called the normal.
A .............. mirror is obtained on silvering the outer surface of a part of a hollow glass sphere.
A boy is standing at a distance of 3m in front of a plane mirror. The distance between the boy and his image is ______m.
