Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain with a suitable diagram, how a concave mirror converges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus and centre of curvature of concave mirror in this diagram.
उत्तर
When a parallel beam of light, also parallel to the principle axis, is incident on a concave mirror, it reflects from the mirror and meets at a point called the focus (F) of the concave mirror. So, a concave mirror has a real focus.
Ray diagram- A concave mirror converges a parallel beam of light rays.
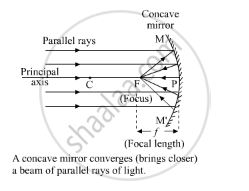
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the focal length of a spherical mirror is 12.5 cm, its radius of curvature will be:
(a) 25 cm
(b) 15 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 35 cm
Which mirror has a wider field of view?
Where would the image be formed by a convex mirror if the object is placed:
between infinity and pole of the mirror?
Draw labelled ray-diagrams to show the formation of image in both the case.
What would your image look like if you stood close to a large:
convex mirror?
If a driver has one convex and one plane rear-view mirror, how would the images in each mirror appear different?
The image formed by a spherical mirror is virtual. The mirror will be:
(a) concave
(b) convex
(c) either concave or convex
(d) metallic
An object 1 cm tall is placed 30 cm in front of a convex mirror of focal length 20 cm. Find the size and position of the image formed by the convex mirror.
Write true or false
At the point of incidence, a line drawn at right angles to the surface, separating the two media, is called the normal.
The focal length of a convex mirror is equal to its radius of curvature.
State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement.
The convex mirror always produces a virtual, diminished and erect image of the object.
