Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
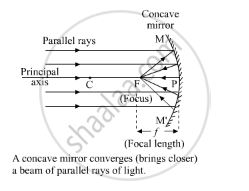
Explain with a suitable diagram, how a concave mirror converges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus and centre of curvature of concave mirror in this diagram.
उत्तर
When a parallel beam of light, also parallel to the principle axis, is incident on a concave mirror, it reflects from the mirror and meets at a point called the focus (F) of the concave mirror. So, a concave mirror has a real focus.
Ray diagram- A concave mirror converges a parallel beam of light rays.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the image formed by a spherical mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a labelled ray diagram to support your answer.
An object is placed at a long distance in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. State the position of its image.
Which type or mirror is usually used as a rear-view mirror in motor cars?
Where would the image be formed by a convex mirror if the object is placed:
between infinity and pole of the mirror?
Draw labelled ray-diagrams to show the formation of image in both the case.
How will you distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror without touching them?
An object is placed at the following distance from a convex lens of focal length 15 cm:
(a) 35 cm
(b) 30 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 10 cm
Which position of the object will produce:
(i) a magnified real image?
(ii) a magnified virtual image?
(iii) a diminished real image?
(iv) an image of same size as the object?
A convex mirror is used
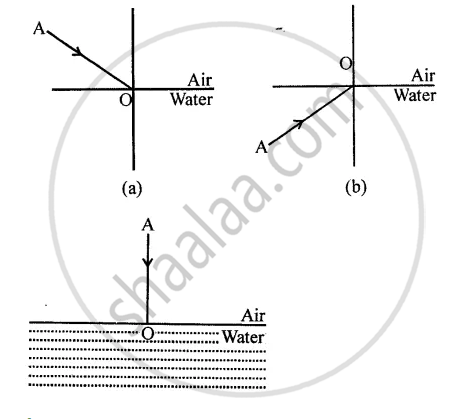
The diagram given below in fig shows a ray of light AO falling on a surface separating two media. Draw the refracted ray in each, case.
Nature of the images formed by a convex mirror is _______.
A convex rearview mirror is preferred over a plane mirror in a car. Why?
