Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram given below in fig shows a ray of light AO falling on a surface separating two media. Draw the refracted ray in each, case.
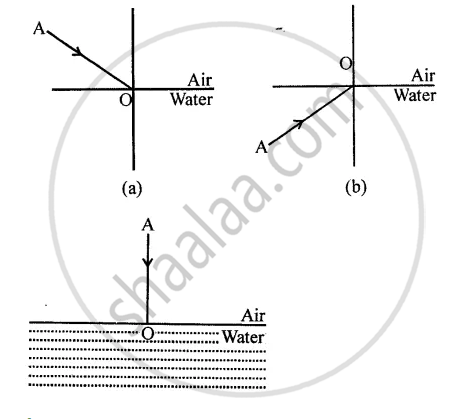
उत्तर
Refracted ray 0 C is shown in each case.
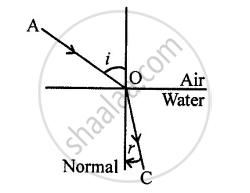
Towards the normal or ∠r < ∠i
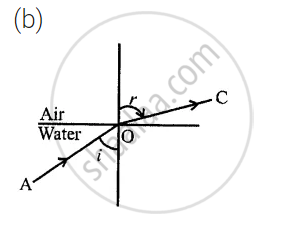
Away from the normal or ∠r > ∠i
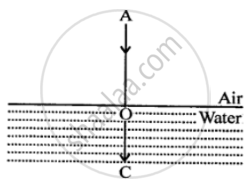
Refracted ray goes undeviated
or
∠i = 0
∠r = 0
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the image formed by a spherical mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a labelled ray diagram to support your answer.
Draw diagram to show the action of convex mirror on a beam of parallel light rays. Mark on this diagram principal axis, focus F, centre of curvature C, pole P and focal length f, of the convex mirror.
A diverging mirror is
(a) a plane mirror
(b) a convex mirror
(c) a concave mirror
(d) a shaving mirror
Where would the image be formed by a convex mirror if the object is placed:
between infinity and pole of the mirror?
Draw labelled ray-diagrams to show the formation of image in both the case.
An object is placed well outside the principal focus of a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram to show how the image is formed, and say whether the image is real or virtual.
What is the effect on the size and position of the image of moving the object (i) towards the lens, and (ii) away from the lens?
The angle formed between the normal and the refracted ray is known as the angle of incidence.
Write true or false
The focal length of a convex mirror is equal to its radius of curvature.
The image formed by these mirrors is ______ than the object.
