Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The diagram given below in fig shows a ray of light AO falling on a surface separating two media. Draw the refracted ray in each, case.
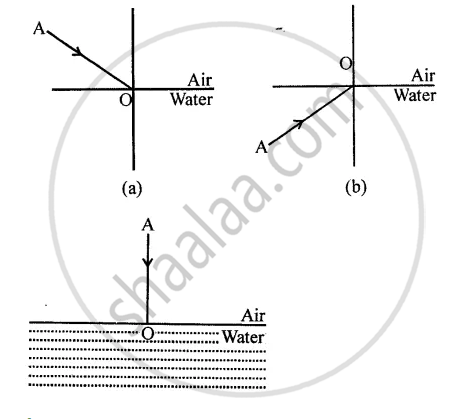
Solution
Refracted ray 0 C is shown in each case.
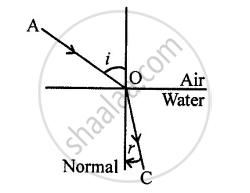
Towards the normal or ∠r < ∠i
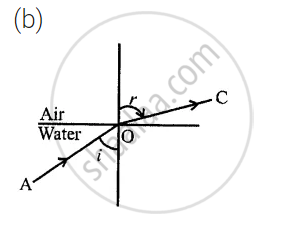
Away from the normal or ∠r > ∠i
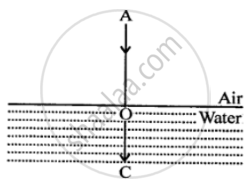
Refracted ray goes undeviated
or
∠i = 0
∠r = 0
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image distance (v) with object distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow, without doing any calculations:
| S. No. | Object distance u(cm) | Image distance v(cm) |
| 1 | −90 | +18 |
| 2 | −60 | +20 |
| 3 | −30 | +30 |
| 4 | −20 | +60 |
| 5 | −18 | +90 |
| 6 | −10 | +100 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of that observation which is not correct. How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(c) Take an appropriate scale to draw ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
Why can you not use a concave mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
Give two uses of a convex mirror. Explain why you would choose convex mirror for these uses.
What would your image look like if you stood close to a large:
convex mirror?
Draw a diagram to represent a convex mirror. On this diagram mark principal axis, principal focus F and the centre of C if the focal length of convex mirror is 3 cm.
A shop security mirror 5.0 m from certain items displayed in the shop produces on-tenth magnification.
What is the radius of curvature of the mirror?
State two uses of a convex mirror.
An object at a distance of +15 cm is slowly moved towards the pole of a convex mirror. The image will get ______.
Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles
Assertion: Convex mirrors are used as a rearview mirror in vehicles for observing traffic at our back.
Reason: A convex mirror has a much larger field of view.
