Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe with a suitable diagram, how a convex mirror diverges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus and centre of curvature of concave mirror in this diagram.
उत्तर
When a parallel beam of light, also parallel to the principle axis, is incident on a convex mirror, it will reflect from the mirror, and the reflected rays will appear to come from a point which is called the focus (F) of the convex mirror. So, a convex mirror has a virtual focus.
Ray diagram- A convex mirror diverges a parallel beam of light rays.
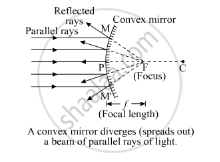
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain with a suitable diagram, how a concave mirror converges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus and centre of curvature of concave mirror in this diagram.
In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at:
(a) a flat surface
(b) a bent-in surface
(c) a bulging-our surface
(d) an uneven surface
A mirror forms an image which is 30 cm from an object and twice its height.
(a) Where must the mirror be situated?
(b) What is the radius of curvature?
(c) Is the mirror convex or concave?
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image in a convex-mirror when the object is at infinity. Mark clearly the pole and focus of the mirror in the diagram.
Two big mirrors A and B are fitted side by side on a wall. A man is standing at such a distance from the wall that he can see the erect image of his face in both the mirrors. When the man starts walking towards the mirrors, he find that the size of his face in mirror A goes on increasing but that in mirror B remains the same.
(a) mirror A is concave and mirror B is convex
(b) mirror A is plane and mirror B is concave
(c) mirror A is concave and mirror B is plane
(d) mirror A is convex and mirror B is concave
A convex mirror used as a rear-view mirror in a car has a radius of curvature of 3 m. If a bus is located at a distance of 5 m from this mirror, find the position of image. What is the nature of the image?
Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed:
between F1 and the optical centre O of the lens.
Which of the above two cases shows the use of convex lens as a magnifying glass? Give reasons for your choice.
An object is placed well outside the principal focus of a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram to show how the image is formed, and say whether the image is real or virtual.
Assertion: Convex mirrors are used as a rearview mirror in vehicles for observing traffic at our back.
Reason: A convex mirror has a much larger field of view.
The image formed by a convex mirror is always ______.
