Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the following diagram. MM' is a concave mirror and AB is an object. Draw on your answer-sheet a ray diagram to show the formation of image of this object.
Solution
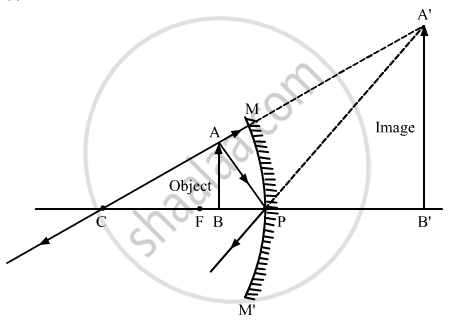
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
To determine the approximate value of the focal length of a given concave mirror, you focus the image of a distant object formed by the mirror on a screen. The image obtained on the serene, as compared to the object is always:
(a) Laterally inverted and diminished
(b) Inverted and diminished
(c) Erect and diminished
(d) Erect and highly diminished
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.
To construct ray diagrams, two rays of light are generally so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from a mirror. Choose two such rays and state the path/direction of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the position and nature of the image of an object placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm.
Three students A, B and C focussed a distant building on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. To determine focal length of the concave mirror they measured the distances as given below:
Student A : From mirror to the screen
Student B : From building to the screen
Student C : From building to the mirror
Who measured the focal length correctly ;
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms a real image equal in size to the object?
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays:
For a real object, which of the following can produce a real image?
A concave mirror of focal length 20 cm forms an image having twice the size of object. For the virtual position of object, the position of object will be at ______.
Which of the following mirror is used by a dentist to examine a small cavity in a patient’s teeth?
