Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
A ray of light is incident on a convex mirror as shown. Redraw the diagram and complete the path of this ray after reflection from the mirror. Mark angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.

Solution 1
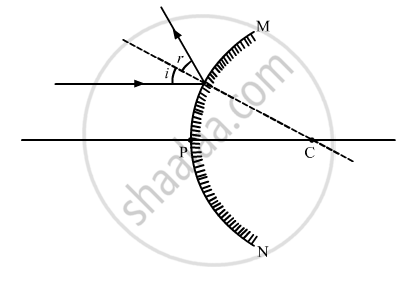
Solution 2
A light ray is incident on a convex mirror parallel to the principal axis. The ray diagram is shown below.

In the above diagram, ‘i’ is the angle of incidence, ‘r’ is the angle of reflection, 'F' is the Focus, 'C' is the Centre of Curvature and 'P' is the Pole.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
To construct ray diagrams, two rays of light are generally so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from a mirror. Choose two such rays and state the path/direction of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the position and nature of the image of an object placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should the position of the object be relative to the mirror? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
For what position of an object, a real and diminished image is formed by a concave mirror?
At what distance from a concave mirror focal length 10 cm should an object 2 cm long be placed in order to get an erect image 6 cm tall?
When an object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror, its image is formed at 10 cm in front of the mirror. Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
An object is placed just outside the principal focus of concave mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show how the image is formed, and describe its size, position and nature.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image. What happens to the image as the object is moved away from the mirror?
A student obtained a sharp image of the grills of a window on a screen using a concave mirror. His teacher remarked that for getting better results a well lit distant object (preferably the sun) should be focussed on the screen. What should be done for this purpose?
(A) Move the screen slightly away from the mirror
(B) Move the mirror slightly towards the screen
(C) Move the screen and the mirror away from the object
(D) Move the screen and the mirror towards the object
Define principal focus of the concave mirror.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Shaving mirror
