English Medium
Academic Year: 2014-2015
Date: March 2015
Advertisements
Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of butane, C4H10.
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Name two simple organisms having the ability of regeneration.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Which of the following are always at the second tropic level of food chains?
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Why is sustainable management of natural resources necessary?
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
Out of the two-reuse and recycle-which, in your opinion, is better to practise? Give reason.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
What is meant by biodiversity? List two advantages of conserving forests and wild life.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
Write the name and general formula of a chain of hydrocarbons in which an addition reaction with hydrogen is possible. State the essential condition for an addition reaction. Stating this condition, write a chemical equation giving the name of the reactant and the product of the reaction.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
List two tests for experimentally distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid and describe how these tests are performed.
Chapter:
Given below are some elements of the modern periodic table. Atomic number of the element is given in parentheses.
A(4), B(9), C(14), D(19), E(20)
(a) Select the element that has one electron in the outermost shell. Also, write the electronic configuration of this element.
(b) Which two elements amongst these belong to the same group? Give reasons for your answer.
(c) Which two elements amongst these belong to the same period? Which one of the two has bigger atomic radius?
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Taking the example of an element of atomic number 16, explain how the electronic configuration of the atom of an element relates to its position in the modern periodic table and how valency of an element is calculated on the basis of its atomic number.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Name the parts A, B and C shown in the diagram and write their functions.
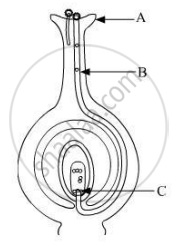
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
List any four methods of contraception used by humans. State in brief two advantages of adopting such preventive methods.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Advertisements
What are chromosomes?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Explain how, in sexually reproducing organisms, the number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Explain the following:- Speciation
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
List four factors responsible for speciation.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Explain the following:- Natural Selection
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Explain with an example for the given, how the following provides evidence in favor of evolution in organisms :
Homologous organs
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Explain with an example for the given, how the following provides evidence in favor of evolution in organisms :
Analogous organs
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Explain with an example for the given, how the following provides evidence in favor of evolution in organisms :
Fossils
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
With the help of scattering of light, explain the reason for the difference in colours of the Sun as it appears during sunset/sunrise and noon.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
An object of height 5 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. If the distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 20 cm, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed using the lens formula.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances with the help of one example each.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
List two changes in habit that people must adopt to dispose of nonbiodegradable waste, for saving the environment.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
Write the importance of ciliary muscles in the human eye. Name the defect of vision that arises due to gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles. What types of lenses are required by the person suffering from this defect to see the objects clearly?
Akshay, sitting in the last row in his class, could not see clearly the words write on the blackboard. When the teacher noticed it, he announced if any student sitting in the front row could volunteer to exchange his seat with Akshay. Salman immediately agreed to exchange his seat with Akshay. He could now see the words written on the blackboard clearly. The teacher thought it fit to send the message to Akshay’s parents advising them to get his eyesight checked.
In the context of the above event, answer the following questions:-
(a) Which defect of vision is Akshay suffering from? Which type of lens is used to correct this defect?
(b) State the values displayed by the teacher and Salman.
(c) In your opinion, in what way can Akshay express his gratitude towards the teacher and Salman?
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
What is meant by a power of a lens? Define its SI unit.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
You have two lenses A and B of focal lengths +10 cm and –10 cm, respectively. State the nature and power of each lens. Which of the two lenses will form a virtual and magnified image of an object placed 8 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to its principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position and the size of the image.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
How do Mendel’s experiments show that the traits may be dominant or recessive?
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Name the human male reproductive organ that produces sperms and also secretes a hormone. Write the functions of the secreted hormone.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where
i. fertilisation takes place
ii. implantation of the fertilised egg occurs
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Explain how the embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Both soap and detergent are some type of salts. What is the difference between them?
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Describe in brief the cleansing action of soap.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Why do soaps not form lather in hard water?
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
List two problems that arise due to the use of detergents instead of soaps.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Advertisements
A student traces the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab for the different values of angle of incidence. He observes all possible precautions at each step of the experiment. At the end of the experiment, on analyzing the measurements, which of the following conclusions is he likely to draw?
(A) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
(B) ∠i < ∠e < ∠r
(C) ∠i > ∠e > ∠r
(D) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student traces the path of a ray of light through a triangular glass prism for different values of angle of incidence. On analyzing the ray diagrams, which one of the following conclusions is he likely to draw?
(A) The emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray.
(B) The emergent ray bends at an angle to the direction of the incident ray.
(C) The emergent ray and the refracted ray are at right angles to each other.
(D) The emergent ray is perpendicular to the incident ray.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
A student obtains a sharp image of the distant window (W) of the school laboratory on the screen (S) using the given concave mirror (M) to determine its focal length. Which of the following distances should he measure to get the focal length of the mirror?
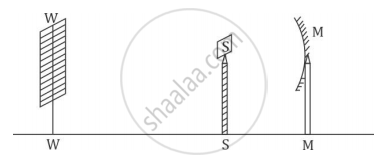
MW
MS
SW
MW-WS
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student used a device (X) to obtain/focus the image of a well illuminated distant building on a screen (S) as shown below in the diagram. Select the correct statement about the device (X).

This device is a concave lens of focal length 8 cm.
This device is a convex mirror of focal length 8 cm.
This device is a convex lens of focal length 4 cm.
This device is a convex lens of focal length 8 cm.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Given below is the list of vegetables available in the market. Select from these the two vegetables having homologous structures:
Potato, sweet potato, ginger, radish, tomato, carrot, okra (Lady’s finger)
(A) Potato and sweet potato
(B) Radish and carrot
(C) Okra and sweet potato
(D) Potato and tomato
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
A student was asked to observe and identify the various parts of an embryo of a red kidney bean seed. He identified the parts and listed them as under:
I. Tegmen
II. Testa
III. Cotyledon
IV. Radicle
V. Plumule
The correctly identified parts among these are
(A) I, II and III
(B) II, III and IV
(C) III, IV and V
(D) I, III, IV and V
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
While preparing soap a small quantity of common salt is generally added to the reaction mixture of vegetable oil and sodium hydroxide. Which one of the following may be the purpose of adding common salt?
(A) To reduce the basic nature of the soap
(B) To make the soap neutral
(C) To enhance the cleansing power of the soap
(D) To favour the precipitation of the soap
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student takes about 4 ml of distilled water in four test tubes marked P, Q, R and S. He then dissolves in each test tube an equal amount of one salt in one test tube, namely sodium sulphate in P, potassium sulphate in Q, calcium sulphate in R and magnesium sulphate in S. After that he adds an equal amount of soap solution in each test tube. On shaking each of these test tubes well, he observes a good amount of lather (foam) in the test tube marked
(A) P and Q
(B) Q and R
(C) P, Q and S
(D) P, R and S
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
What do we observe on pouring acetic acid on red and blue litmus papers?
(A) Red litmus remains red and blue litmus turns red.
(B) Red litmus turns blue and blue litmus remains blue.
(C) Red litmus turns blue and blue litmus turns red.
(D) Red litmus becomes colourless and blue litmus remains blue.
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
Students were asked to observe the permanent slides showing different stages of budding in yeast under high power of a microscope.
(A) Which adjustment screw (coarse/fine) were you asked to move to focus the slides?
(B) Draw three diagrams in correct sequence showing budding in yeast.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
When you add sodium hydrogen carbonate to acetic acid in a test tube, a gas liberates immediately with brisk effervescence. Name this gas. Describe the method of testing this gas.
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
A 4 cm tall object is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. The distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 12 cm and its sharp image is formed at a distance of 24 cm from it on a screen on the other side of the lens. If the object is now moved a little away from the lens, in which way (towards the lens or away from the lens) will he have to move the screen to get a sharp image of the object on it again? How will the magnification of the image be affected?
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 10 Science with solutions 2014 - 2015
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 10 Science-2015 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Science, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 10.
How CBSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Science will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
