Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How do Mendel’s experiments show that the traits may be dominant or recessive?
Solution
Mendel crossed purebred tall pea plants with purebred dwarf pea plants and found that only tall pea plants were produced in the first generation, and there were no dwarf pea plants. He concluded that the first generation showed the traits of only one of the parent plants tallness. The trait of the other parent plant dwarfness did not show up in the progeny of the first generation.
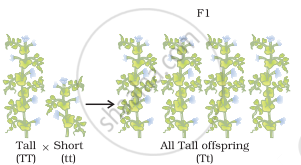
He then crossed the tall pea plants obtained in the first generation (F1 generation) and found that both tall plants and dwarf plants were obtained in the second generation (F2 generation) in the ratio of 3 : 1. Mendel noted that the dwarf trait of the parent pea plant which disappeared in the first generation progeny reappeared in the second generation. In this way, Mendel’s experiments with tall and dwarf pea plants showed that the traits may be dominant and recessive.

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is a gene?
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits – blood group A or O – is dominant? Why or why not?
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as:
What constitutes the link between one generation and the next?
State whether the following statement is true or false :
The sex of an infant is not a case of inheritance of characteristics.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word .
In pea plants, the gene for dwarfness is ..............whereas that for tallness is ............ .
Give the contrasting traits of the following characters in pea plant and mention which is dominant and which is recessive :
Round seed
State Mendel's second law of inheritance.
In order to ensure that he had pure-breeding plants for his experiments, Mendel :
(a) cross-fertilised each variety with each other
(b) let each variety self fertilise for several generations
(c) removed the female parts of the plants
(d) removed the male parts of the plants.
The following results were obtained by a scientist who crossed the F1 generation of pure-breeding parents for round and wrinkled seeds.
| Dominant trait | Recessive trait | No. of F2 offspring |
| Round seeds | Wrinkled seeds | 7524 |
From these results, it can be concluded that the actual number of round seeds he obtained was ______
What are the possible blood groups likely to be inherited by children born to a group A mother and a group B father? Explain your reasoning.
A person first crossed pure-bred pea plants having round-yellow seeds with pure-bred pea plants having wrinkled-green seeds and found that only A-B type of seeds were produced in the F1 generation. When F1generation pea plants having A-B type of seeds were cross-bred by self-pollination, then in addition to the original round-yellow and wrinkled-green seeds, two new varieties A-D and C-B type of seeds were also obtained.
(a) What are A-B type of seeds?
(b) State whether A and B are dominant traits or recessive traits.
(c) What are A-D type of seeds?
(d) What are C-B type of seeds?
(c) Out of A-B and A-D types of seeds, which one will be produced in (i) minimum numbers, and (ii) maximum numbers, in the F2 generation?
One of the following traits cannot be inherited. This one is :
(a) colour of eyes
(b) colour of skin
(c) size of body
(d) nature of hair
The farmers have been cultivating a food plant X for over two thousand years and have produced as many as five entirely different looking vegetables A, B, C, D and E from it.
(a) What could the plant X be?
(b) What are A, B, C, D and E?
(c) What is the process of evolution involved in this example known as?
List two differences in tabular form between dominant trait and recessive traits. What percentage/proportion of the plants in the F2 generation/progeny were round, in Mendel's cross between round and wrinkled pea plants?
Define Heredity. Give two examples.
Answer the following question.
Why are the traits acquired during the life-time-of-an individual not inherited? Explain.
In the following Question, the Assertion and Reason have been put forward. Read the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Assertion: When pure breed tall plants are crossed with pure breed short plants, all the plants in F1 progeny are tall. When the tall plants of F1 progeny are crossed, short plants re-appear in F2 progeny.
Reason: Traits are independently inherited.
A cross between a tall plant (TT) and short pea plant (tt) resulted in progeny that were all tall plants because
What are the components of the DNA molecule?
