Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are the components of the DNA molecule?
Solution
Phosphoric acid, pairs of nitrogenous bases, and deoxyribose sugar are components of DNA molecule.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In one of his experiments with pea plants, Mendel observed that when a pure tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant in the first generation, F1, only tall plants appear.
(a) What happens to the traits of the dwarf plants in this case?
(b) When the F1-generation plants were self-fertilised, he observed that in the plants of the second generation, F2, both tall plants and dwarf plants were present. Why it happened? Explain briefly.
How did Mendel interpret his results to show that traits may be dominant or recessive? Describe briefly.
A pea plant with blue colour flower denoted by BB is cross-bred with a pea plant with white flower denoted by ww.
(a) What is the expected colour of the flowers in their F1 progeny?
(b) What will be the percentage of plants bearing white flower in F2 generation, when the flowers of F1 plants were selfed?
(c) State the expected ratio of the genotype BB and Bw in the F2 progeny.
A cross was made between pure breeding pea plants one with round and green seeds and the other with wrinkled and yellow seeds.
(a) Write the phenotype of F1 progeny. Give reason for your answer.
(b) Write the different types of F2 progeny obtained along with their ration when F1 progeny was selfed.
Mendel in one of his experiments with pea plants crossed a variety having round seed with one having wrinkled seeds. Write his observations, giving reasons, of F1 and F2 progeny
A study found that children with light-coloured eyes are likely to have parents with light-coloured eyes. On this basis, can we say anything about whether the light eye colour trait is dominant or recessive? Why or why not?
Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat colour in dogs.
What constitutes the link between one generation and the next?
Using height (tallness/dwarfness) of a plant as an example, show that genes control the characteristics or traits in an organism.
In the F2 generation of a cross, progeny having different traits are produced in the ratio 3 : 1. State whether it is a monohybrid cross or a dihybrid cross? Give one example of such a cross.
What sizes of plants are produced if both parents have genes Tt?
Give the contrasting traits of the following characters in pea plant and mention which is dominant and which is recessive :
Round seed
What are the units of heredity.
State Mendel's second law of inheritance.
A cross between two individuals results in a ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 for four possible phenotypes of progeny. This is an example of a ______
In the human blood grouping, the four basic blood types are type A, type B, type AB, and type O. The blood proteins A and B are :
(a) simple dominant and recessive traits
(b) incomplete dominant traits
(c) codominant traits
(d) sex-linked traits
A cross between a tall plant (TT) and short plant (tt) resulted in progeny that were all tall plants because :
(a) tallness is the dominant trait
(b) shortness is the dominant trait
(c) tallness is the recessive trait
(d) height of plant is not governed by gene T or t
In humans, if gene B gives brown eyes and gene b gives blue eyes. What will be the colour of eyes of the persons having the following combination of genes?
(a) Bb
(b) bb
(c) BB
A red-haired woman marries a brown-haired man, and all the children are brown haired. Explain this genetically.
A person first crossed pure-bred pea plants having round-yellow seeds with pure-bred pea plants having wrinkled-green seeds and found that only A-B type of seeds were produced in the F1 generation. When F1generation pea plants having A-B type of seeds were cross-bred by self-pollination, then in addition to the original round-yellow and wrinkled-green seeds, two new varieties A-D and C-B type of seeds were also obtained.
(a) What are A-B type of seeds?
(b) State whether A and B are dominant traits or recessive traits.
(c) What are A-D type of seeds?
(d) What are C-B type of seeds?
(c) Out of A-B and A-D types of seeds, which one will be produced in (i) minimum numbers, and (ii) maximum numbers, in the F2 generation?
Mendel first crossed pure-bred pea plants having round-yellow seeds with pure-bred pea plants having wrinkled-green seeds and found that only round-yellow seeds were produced in the F1 generation. When F1generation pea plants having round-yellow seeds were cross-bred by self pollination, then peas having round-yellow seeds, round green seeds, wrinkled-yellow seeds and wrinkled-green seeds were produced. Mendel collected a total of 2160 seeds.
(a) What will be the number of (i) round green seeds (ii) wrinkled green seeds (iii) round yellow seeds, and (iv) wrinkled-yellow seeds?
(b) Which 'ratio' as established by Mendel have you made use of in answering the part (a) above?
The term 'father of genetics' is used for the scientist :
(a) Morgan
(b) Mendel
(c) Darwin
(d) Marie Curie
One of the following traits cannot be inherited. This one is :
(a) colour of eyes
(b) colour of skin
(c) size of body
(d) nature of hair
One of the following traits of the parents cannot be passed on to their future generations. This trait is :
(a) cleft chin
(b) pointed chin
(c) scarred chin
(d) broad chin
Explain Mendel’s law of independent inheritance. Give one example.
Mendel, in one of his experiments with pea plants, crossed a variety of pea plant having round seeds with one having wrinkled seeds. State Mendel’s observations giving reasons of F1 and F2 progeny of this cross. Also, list any two contrasting characters, other than round seeds of pea plants that Mendel used in his experiments.
Define Heredity. Give two examples.
Answer the following question.
Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 and F2 generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in F2 generation plants.
Answer the following question.
Why are the traits acquired during the life-time-of-an individual not inherited? Explain.
____________ refers to the transmission of genetic information from parental generation to next generation.
What will be the number of chromosomes present in each gamete produced by the plants if the palisade cells of a species of the plant contain 28 chromosomes in all?
Two pink coloured flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink and 1 white flower progeny. The nature of the cross will be
In human males all the chromosomes are paired perfectly except one. This/these unpaired chromosome is/are
- large chromosome
- small chromosome
- Y-chromosome
- X-chromosome
In the following figure showing a germinating gram seed, name the parts labelled as A, B and C:
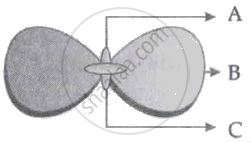
Why is Part 'B' considered to be important during germination?
Mendel crossed pea plants with two pairs of contrasting characters.
| RRYY | × |
rryy |
| Round, Yellow | Wrinkled, Green |
He observed 4 types of combinations in F2 generation. Which of the combinations were new? Write the conclusion drawn by this experiment.
Name the following:
The basic units of heredity.
