Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define Heredity. Give two examples.
Solution
- Heredity is the transmission of physical or mental traits from parents to offsprings.
- Example: Attached ear-lobes, Rolling tongue.
RELATED QUESTIONS
"A trait may be inherited, but may not be expressed." Justify this statement with the help of a suitable example.
In one of his experiments with pea plants, Mendel observed that when a pure tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant in the first generation, F1, only tall plants appear.
(a) What happens to the traits of the dwarf plants in this case?
(b) When the F1-generation plants were self-fertilised, he observed that in the plants of the second generation, F2, both tall plants and dwarf plants were present. Why it happened? Explain briefly.
Define heredity.
Mendel crossed tall pea plants with dwarf pea plants in his experiment. Write his observations giving reason on the F1 and F2 generations.
List any two contrasting characters other than height that Mendel used in his experiments in pea plants.
Mendel in one of his experiments with pea plants crossed a variety having round seed with one having wrinkled seeds. Write his observations, giving reasons, of F1 and F2 progeny
List any two contrasting characters other than roundness of pea plants that Mendel used in his experiments with pea plants.
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as:
How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
To perform an experiment to identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed, first of all you require a dicot seed. Select dicot seeds from the following group:
Wheat, Gram, Maize, Pea, Barley, Ground-nut
(A) Wheat, Gram and Pea
(B) Gram, Pea and Ground-nut
(C) Maize, Pea and Barley
(D) Gram, Maize and Ground-nut
State whether the following statement is true or false :
The sex of an infant is not a case of inheritance of characteristics.
The gene for red hair is recessive to the gene for black hair. What will be the hair colour of a person if he inherits a gene for red hair from his mother and a gene for black hair from his father?
A man having blood group O marries a woman having blood group B and they have a daughter. What will be the blood group of the daughter?
What sizes of plants are produced if both parents have genes Tt?
Gregor Mendel's first law of genetics states "Of a pair of contrasted characters, only one can be represented in a gamete by its internal 'factor' State where these factors are found in gametes.
Give the contrasting traits of the following characters in pea plant and mention which is dominant and which is recessive:
Yellow seed
State Mendel's second law of inheritance.
A cross between two individuals results in a ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 for four possible phenotypes of progeny. This is an example of a ______
A trait in an organism is influenced by ______
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) for every hormone there is a gene
(b) for every protein there is a gene
(c) for production of every enzyme there is a gene
(d) for every type of fat there is a gene
In humans, if gene B gives brown eyes and gene b gives blue eyes. What will be the colour of eyes of the persons having the following combination of genes?
(a) Bb
(b) bb
(c) BB
Pure-bred pea plants A are crossed with pure-bred pea plants B. It is found that the plants which look like A do not appear in F1 generation but re-emerge in F2 generation. Which of the plants A and B are : (i) tall, and (ii) dwarf? Give reason for your answer.
A red-haired woman marries a brown-haired man, and all the children are brown haired. Explain this genetically.
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits-blood group A or O - is dominant? Why or why not?
Only one of the following characteristic of the parents can be inherited by their children. This one is :
(a) deep scar on chin
(b) snub nose
(c) technique of swimming
(d) cut nose
List two differences in tabular form between dominant trait and recessive traits. What percentage/proportion of the plants in the F2 generation/progeny were round, in Mendel's cross between round and wrinkled pea plants?
Explain the mechanism of hereditary changes.
Mendel, in one of his experiments with pea plants, crossed a variety of pea plant having round seeds with one having wrinkled seeds. State Mendel’s observations giving reasons of F1 and F2 progeny of this cross. Also, list any two contrasting characters, other than round seeds of pea plants that Mendel used in his experiments.
Answer the following question.
Why are the traits acquired during the life-time-of-an individual not inherited? Explain.
What is genetics?
Who is the pioneer of modern genetics?
In humans, if gene B gives brown eyes and gene b gives blue eyes, what will be the colour of eyes of the persons having combinations
(i) Bb and (ii) BB?
In the following figure showing a germinating gram seed, name the parts labelled as A, B and C:
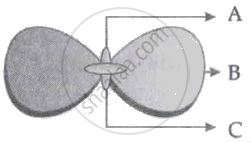
Why is Part 'B' considered to be important during germination?
A cross between pea plant with white flowers (vv) and pea plant with violet flowers (VV) resulted in F2 progeny in which ratio of violet (VV) and white (vv) flowers will be ______.
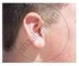
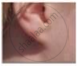
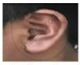
Figures (a) to (d) given below represent the type of ear lobes present in a family consisting of 2 children - Rahul, Nisha and their parents.
|
(a) Rahul's Father |
(b) Rahul |
(c) Rahul's Mother |
(d) Rahul's sister Nisha |
|
(e) |
(f) |
||
| Types of ear lobes | |||
Excited by his observation of different types of ear lobes present in his family, Rahul conducted a survey of the type of ear lobes found {Figure (e) and (f)} in his classmates. He found two types of ear lobes in his classmates as per the frequency given below:
| Sex | Free | Attached |
| Male | 36 | 14 |
| Female | 31 | 19 |
On the basis of the above data answer the following questions.
- Which of the two characteristics - ‘free ear lobe’ or ‘attached ear lobe’ appears to be dominant in this case? Why?
- Is the inheritance of the free ear lobe linked with the sex of the individual? Give a reason for your answer.
- What type of ear lobe is present in father, mother, Rahul and his sister Nisha? Write the genetic constitution of each of these family members which explains the inheritance of this character in this family.
(Gene for the Free ear lobe is represented by F and the gene for the attached ear lobe is represented by f for writing the genetic constitution).
OR
Suresh’s parents have attached ear lobes. What type of ear lobe can be seen in Suresh and his sister Siya? Explain by giving the genetic composition of all.
Name the following:
The basic units of heredity.