Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Who is the pioneer of modern genetics?
Solution
Gregor Johann Mendel
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
"A trait may be inherited, but may not be expressed." Justify this statement with the help of a suitable example.
In a monohybrid cross between tall pea plants (TT) and short pea plants (tt), a scientist obtained only tall pea plants (Tt) in the F1 generation. However, on selfing the F1 generation pea plants, he obtained both tall and short plants in F2 generation. On the basis of above observations with other angiosperms also, can the scientist arrive at a law? If yes, explain the law. If not, give justification for your answer.
Define heredity.
List any two contrasting characters other than roundness of pea plants that Mendel used in his experiments with pea plants.
To perform an experiment to identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed, first of all you require a dicot seed. Select dicot seeds from the following group:
Wheat, Gram, Maize, Pea, Barley, Ground-nut
(A) Wheat, Gram and Pea
(B) Gram, Pea and Ground-nut
(C) Maize, Pea and Barley
(D) Gram, Maize and Ground-nut
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding pea plants bearing violet flowers with pea plants bearing white flowers. What will be the result in F1 progeny?
Mendel said that the characteristics or traits of organisms are carried from one generation to the next by internal factors which occur in pairs. What is the modern name for these factors?
What type of plants were used by Mendel for conducting his experiments on inheritance?
The gene for red hair is recessive to the gene for black hair. What will be the hair colour of a person if he inherits a gene for red hair from his mother and a gene for black hair from his father?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word .
In pea plants, the gene for dwarfness is ..............whereas that for tallness is ............ .
Name the scientist who gave the laws of inheritance.
In the F2 generation of a cross, progeny having different traits are produced in the ratio 3 : 1. State whether it is a monohybrid cross or a dihybrid cross? Give one example of such a cross.
What is the genotype of tall plants which always produced tall offspring
Gregor Mendel's first law of genetics states "Of a pair of contrasted characters, only one can be represented in a gamete by its internal 'factor Give the modern name for this 'factor'.
Why did Mendel choose pea plants for conducting his experiments on inheritance?
How do Mendel's experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
When two parents are crossed, the offspring are referred to as :
recessives
test cross
F1 generation
F2 generation
A cross between a tall plant (TT) and short plant (tt) resulted in progeny that were all tall plants because :
(a) tallness is the dominant trait
(b) shortness is the dominant trait
(c) tallness is the recessive trait
(d) height of plant is not governed by gene T or t
Select the statements that describe characteristics of genes :
(i) genes are specific sequences of bases in a DNA molecule.
(ii) a gene does not code for proteins.
(iii) in individuals of a given species, a specific gene is located on a particular chromosome.
(iv) each chromosome has only one gene..
A person first crossed pure-bred pea plants having round-yellow seeds with pure-bred pea plants having wrinkled-green seeds and found that only A-B type of seeds were produced in the F1 generation. When F1generation pea plants having A-B type of seeds were cross-bred by self-pollination, then in addition to the original round-yellow and wrinkled-green seeds, two new varieties A-D and C-B type of seeds were also obtained.
(a) What are A-B type of seeds?
(b) State whether A and B are dominant traits or recessive traits.
(c) What are A-D type of seeds?
(d) What are C-B type of seeds?
(c) Out of A-B and A-D types of seeds, which one will be produced in (i) minimum numbers, and (ii) maximum numbers, in the F2 generation?
Pure-bred round-yellow pea seeds have genotype RRYY and the pure-bred wrinkled-green pea seeds have genotype rryy. Keeping this in mind, write the phenotypes of the following genotypes of hybrid pea seeds :
(a) Rryy
(b) rrYy
(c) rrYY
(d) RrYy
(e) RRyy
One of the following traits of the parents cannot be passed on to their future generations. This trait is :
(a) cleft chin
(b) pointed chin
(c) scarred chin
(d) broad chin
The farmers have been cultivating a food plant X for over two thousand years and have produced as many as five entirely different looking vegetables A, B, C, D and E from it.
(a) What could the plant X be?
(b) What are A, B, C, D and E?
(c) What is the process of evolution involved in this example known as?
List two differences in tabular form between dominant trait and recessive traits. What percentage/proportion of the plants in the F2 generation/progeny were round, in Mendel's cross between round and wrinkled pea plants?
Explain Mendel’s law of independent inheritance. Give one example.
Hereditary characters are transferred from parents to offspring by ______ hence they are said to be structural and functional units of heredity.
Define Heredity. Give two examples.
Answer the following question.
Why are the traits acquired during the life-time-of-an individual not inherited? Explain.
In humans, if gene B gives brown eyes and gene b gives blue eyes, what will be the colour of eyes of the persons having combinations
(i) Bb and (ii) BB?
Two pink coloured flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink and 1 white flower progeny. The nature of the cross will be
A cross between a tall plant (TT) and short pea plant (tt) resulted in progeny that were all tall plants because
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
If a tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant then, what percentage of F1 and F2 generation respectively will be tall?
A cross between pea plant with white flowers (vv) and pea plant with violet flowers (VV) resulted in F2 progeny in which ratio of violet (VV) and white (vv) flowers will be ______.
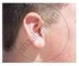
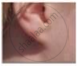
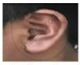
Figures (a) to (d) given below represent the type of ear lobes present in a family consisting of 2 children - Rahul, Nisha and their parents.
|
(a) Rahul's Father |
(b) Rahul |
(c) Rahul's Mother |
(d) Rahul's sister Nisha |
|
(e) |
(f) |
||
| Types of ear lobes | |||
Excited by his observation of different types of ear lobes present in his family, Rahul conducted a survey of the type of ear lobes found {Figure (e) and (f)} in his classmates. He found two types of ear lobes in his classmates as per the frequency given below:
| Sex | Free | Attached |
| Male | 36 | 14 |
| Female | 31 | 19 |
On the basis of the above data answer the following questions.
- Which of the two characteristics - ‘free ear lobe’ or ‘attached ear lobe’ appears to be dominant in this case? Why?
- Is the inheritance of the free ear lobe linked with the sex of the individual? Give a reason for your answer.
- What type of ear lobe is present in father, mother, Rahul and his sister Nisha? Write the genetic constitution of each of these family members which explains the inheritance of this character in this family.
(Gene for the Free ear lobe is represented by F and the gene for the attached ear lobe is represented by f for writing the genetic constitution).
OR
Suresh’s parents have attached ear lobes. What type of ear lobe can be seen in Suresh and his sister Siya? Explain by giving the genetic composition of all.